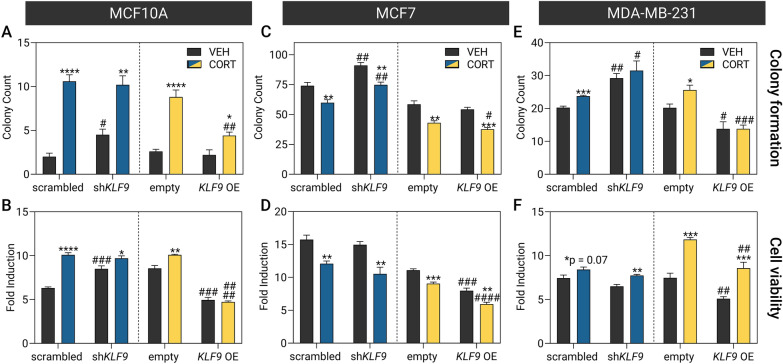
Fig. 5.
KLF9 restricts breast epithelial cell survival and proliferation. Effects of CORT treatment and KLF9 knockdown (blue) or overexpression (yellow) on A, C, E cell survival and B, D, F viability of breast epithelial cell lines as evaluated using assays based on colony formation and resazurin reduction, respectively. The cells were treated with vehicle (100% ethanol) or CORT (100 nM) for 14 d and 96 h for the colony formation and cell viability assay, respectively. In MCF10A, CORT promoted A survival and B proliferation in both knockdown [2-way ANOVA; Colony formation: treatment: P < 0.0001; knockdown: P = 0.2060|Cell viability: treatment: P < 0.0001; Knockdown: P = 0.0004] and overexpression lines [2-way ANOVA; Colony formation: treatment: P < 0.0001; overexpression: P = 0.0005|Cell viability: treatment: P = 0.1045; overexpression: P < 0.0001. In the luminal MCF7 line, CORT treatment diminished C survival and D proliferation in both knockdown [2-way ANOVA; Colony formation: treatment, knockdown: P < 0.0001|Cell viability: treatment: P < 0.0001; knockdown: P = 0.0355] and overexpression lines [2-way ANOVA; colony formation: treatment: P < 0.0001; overexpression: P = 0.0269|Cell viability: treatment: P < 0.0001; overexpression: P < 0.0001]. Finally, in MDA-MB-231 cells, CORT treatment enhanced E colony formation and F proliferation in both KLF9 knockdown [2-way ANOVA; colony formation: treatment, P = 0.1026; knockdown: P = 0.0002|Cell viability: treatment: P = 0.0006; Knockdown: P = 0.0057] and overexpression lines [2-way ANOVA; Colony formation: treatment: P = 0.0986; overexpression: P < 0.0001|Cell viability: treatment, overexpression: P < 0.0001]. Bars represent mean ± SEM with statistically significant differences determined through two-way ANOVA for main effects of treatment or overexpression and Student’s t-test for individual effects of hormone treatment (*) and knockdown or overexpression (#). All experiments were performed with N ≥ 4 replicates