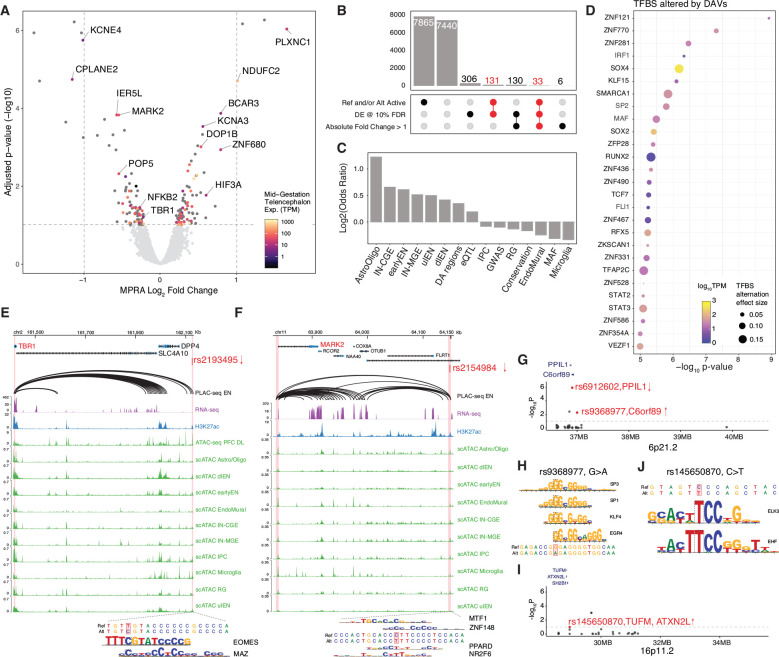
Fig. 3. Identification of differential active variants associated with psychiatric disorders.
(A) Volcano plot showing log2 Fold Change and −log10 adjusted p-value for variants that have enhancer activity from at least one allele. Significant variants (FDR < 0.1) were annotated with PLAC-seq predicted target gene name and color-coded based on target gene expression in mid-gestation telencephalon. Two vertical dashed lines indicate the absolute log2FC of 1. The horizontal dashed line indicates FDR at 10%. (B) Upset plot showing the number of variants (bar) passing combinations of different thresholds (dots and lines below bar). The number of DAVs was highlighted in red. (C) Enrichment log2 odds ratio of DAVs overlapping different features, including combined or separate cell-type-specific DA regions, adult brain eQTL, GWAS of various psychiatric disorders and low-frequency variants with minor allele frequency (MAF) less than 0.01. (D) TFBSs predicted to be altered by DAVs using motifbreakR. Dot color represents TF expression in primary cortical cells, size represents predicted magnitude of binding affinity alternation. TFs were ranked by TFBS alternation significance (−log10p-value, y-axis). (E-F) Genomic browser tracks showing examples of causal regulatory variants and their predicted target genes. The top track shows PLAC-seq chromatin loop in EN (32), the second track shows bulk RNA-seq in primary cortical cells, the third track shows bulk H3K27ac ChIP-seq (31), followed by a track of bulk ATAC-seq in deep-layer cortex (31). The bottom ten tracks show scATAC-seq in human cortex (11). DAV rs2193495 (E), located in a dlEN-specific accessible region, potentially down-regulates TBR1 expression due to the introduction of EOMES and MAZ binding sites. DAV rs2154984 (F) is predicted to regulate MARK2 expression and disrupt MTF1 and ZNF148 and introduce PPARD and NR2F6 binding sites. (G) Manhattan plot of SCZ-associated chromosome band 6p21.2 showing the 38 variants tested. The y-axis shows −log10 of adjusted p-value from MPRA. DAVs are highlighted in red and annotated with their predicted target gene. Arrows indicate the direction of allele effect observed in MPRA. (H) DAV rs9368977 located in 6p21.2 is predicted to disrupt binding of SP3, SP1, KLF4 and EGR4. (I) Manhattan plot of ASD-associated chromosome band 16p11.2 showing the 25 variants tested. The y-axis shows −log10 of adjusted p-value from MPRA. DAVs are highlighted in red and annotated with predicted target genes. The arrow indicates the direction of allele effect observed in MPRA. (J) TFBS altered in rs145650870. The alternative allele favors the binding of EHF and ELK3.