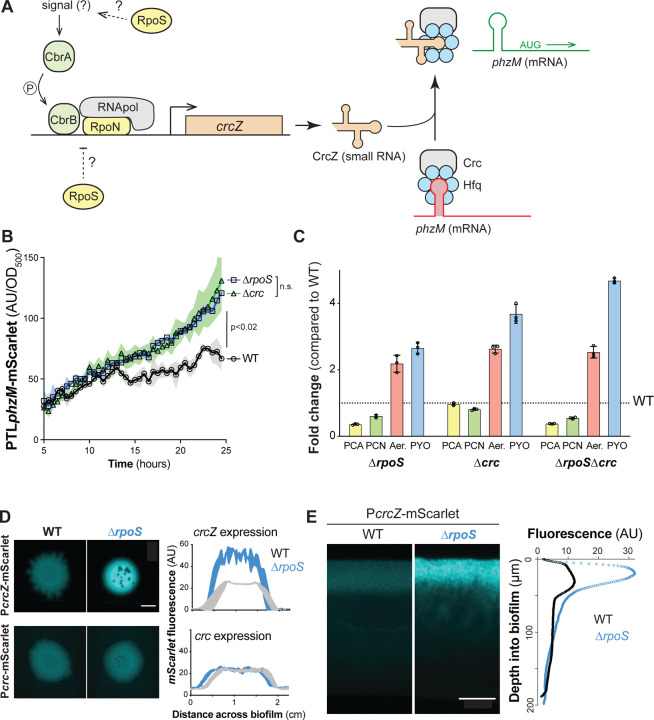
Figure 3. RpoS inhibits phenazine methylation by modulating the carbon catabolite repression pathway at the biofilm-air interface.
(A) Schematic of the P. aeruginosa carbon catabolite repression pathway, which controls translation of phzM in a carbon source-dependent manner. RpoN is the canonical sigma factor that is associated with this pathway and it acts in conjunction with the transcription factor CbrB. When CrcZ levels are low, the Crc/Hfq complex binds to phzM transcript and inhibits translation. When CrcZ levels are high, CrcZ binds and sequesters Crc/Hfq, allowing translation of the phzM transcript. (B) Fluorescence conferred by PTLphzM-mScarlet over time for planktonic cultures of the indicated parent strains. Readings are shown starting at 5 h of incubation, which corresponds to the onset of stationary phase. (C) Changes in production of phenazine derivatives by ∆rpoS, ∆crc, and ∆rpoS∆crc biofilms relative to biofilms formed by WT PA14. Individual points represent biological triplicates and error bars represent standard deviation. (D) Representative whole-biofilm fluorescence images of PA14 WT and ΔrpoS strains expressing mScarlet under control of PcrcZ or Pcrc. mScarlet fluorescence is false-colored cyan. The average levels of fluorescence produced by each strain along the diameter of three independent biofilms with the Pcrc-mScarlet or PcrcZ-mScarlet reporters are shown in the right-hand plots. Scale bar is 5 mm. (E) Fluorescence microscopy of thin sections prepared from WT PA14 and ΔrpoS biofilms expressing PcrcZ-mScarlet. mScarlet fluorescence is false-colored cyan. Average fluorescence across depth is shown in the right-hand plot. In (B) and (D), the average of 3 biological replicates is plotted and shading indicates the standard deviation. p values were calculated using unpaired, two-tailed t-tests. Scale bar is 50 μm.