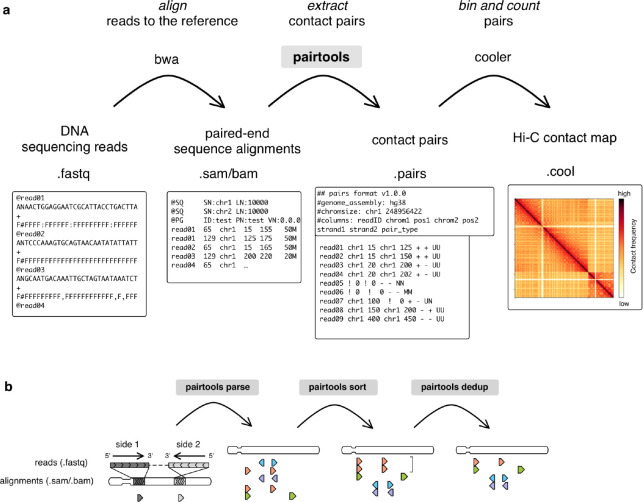
Figure 1. Processing 3C+ data using pairtools.
a. Outline of 3C+ data processing leveraging pairtools. First, a sequenced DNA library is mapped to the reference genome with sequence alignment software, typically using bwa mem for local alignment. Next, pairtools extracts contacts from the alignments in .sam/.bam format. Pairtools outputs a tab-separated .pairs file that records each contact with additional information about alignments. A .pairs file can be saved as a binned contact matrix with counts with other software, such as cooler. The top row describes the steps of the procedure; the middle row describes the software and chain of files; the bottom row depicts an example of each file type.
b. Three main steps of contact extraction by pairtools: parse, sort, and dedup. Parse takes alignments of reads as input and extracts the pairs of contacts. In the illustration, alignments are represented as triangles pointing in the direction of read mapping to the reference genome; each row is a pair extracted from one read. The color represents the genomic position of the alignment with the smallest coordinate, from the leftmost coordinate on the chromosome (orange) to the rightmost coordinate on the chromosome (violet). Sort orders mapped pairs by their position in the reference genome. Before sorting, pairs are ordered by the reads from which they were extracted. After sorting, pairs are ordered by chromosome and genomic coordinate. Dedup removes duplicates (pairs with the same or very close positions of mapping). The bracket represents two orange pairs with very close positions of mapping that are deduplicated by dedup.