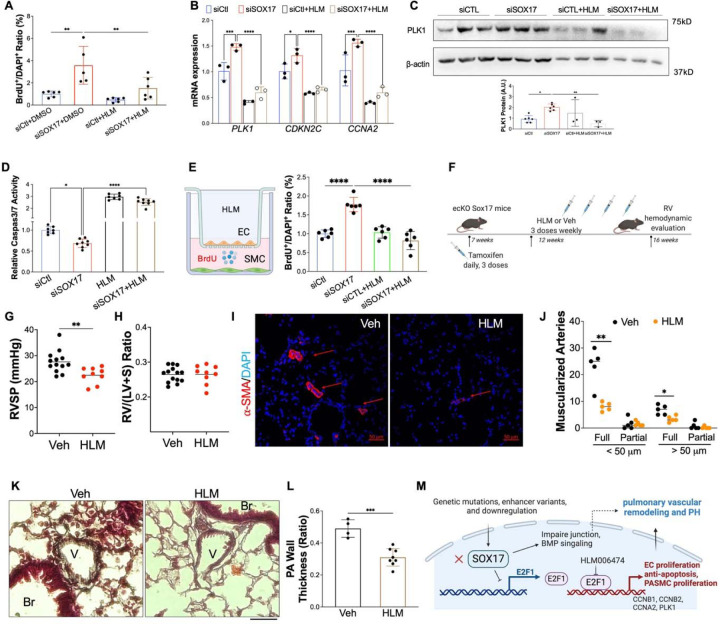
Figure 9. Pharmacological inhibition of E2F1 reduced EC dysfunction and PH development in ecKO Sox17 mice.
(A) E2F1 inhibition reduced EC proliferation measured by BrdU incorporation assay. At 48 hours post-transfection of siRNA against SOX17 or control siRNA, HPVECs were treated with DMSO or HLM for 12 hours in serum/growth factors free medium. 2.5% FBS and BrdU were added in the medium at 4 hours prior to cells harvest. (B) qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated normalization of the expression of genes related to cell proliferation after E2F1 inhibition in HPVECs. At 48 hours post-transfection, HPVECs were treated with DMSO or HLM for 12 hours in serum/growth factors free medium. 2.5% FBS were added in the medium at 4 hours prior to RNA isolation. (C) E2F1 inhibition reduced cell proliferation marker PLK1 expression in SOX17 deficiency in HPVECs. (D) Pharmacological inhibition of E2F1 increased EC apoptosis in SOX17 deficient HPVECs. At 48 hours post-transfection, HPVECs were treated with DMSO or HLM for 12 hours in serum/growth factors free medium, followed by measurement of Caspase 3/7 activities. (E) A diagram showing the strategy of E2F1 inhibition in ecKO Sox17 mice. (F) RVSP was attenuated by E2F1 inhibition in ecKO Sox17 mice. (G) RV hypertrophy was not altered by E2F1 inhibition. (H and I) Muscularization of distal pulmonary arteries were reduced by E2F1 inhibition in ecKO Sox17 mice compared to vehicle. α-SMA+ vessels were quantified in 20 field at 10X magnification per mouse. (J and K) Pentachrome staining showed that E2F1 inhibition by HLM attenuated pulmonary wall thickness. Wall thickness was calculated by the distance between internal wall and external wall divided by the distance between external wall and the center of lumen. Studies were repeated at least 3 times (A, B, D). One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis (A-D) and Student t test (F, G, I, K). *, P< 0.05; **, P< 0.01, ***, P< 0.001, ****, P< 0.0001. Scale bar, 50 μm.