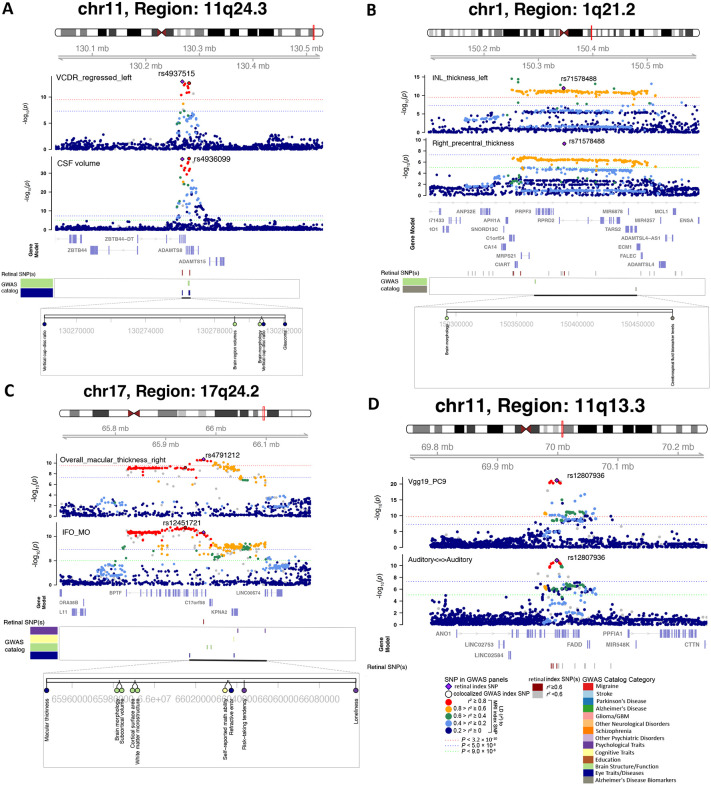
Fig. 4. Selected genetic loci that were associated with both eye and brain imaging traits.
(A) In 11q24.3, we observed shared genetic influences between the vertical cup-to-disc ratio (regressed on disc diameter, left eye, VCDR_regressed_left, index variant rs4937515) and the cerebrospinal fluid volume (CSF volume, index variant rs4936099). Bayesian colocalization analysis suggested the shared causal variant between the two traits (posterior probability PPH4 = 0.997). (B) In 1q21.2, we observed shared genetic influences between the inner nuclear layer (INL) thickness (left eye, INL_thickness_left) and the cortical thickness of the right precentral brain region (Right_precentral_thickness, shared index variant rs71578488, PPH4 = 0.562). In this region, the INL_thickness_left was also in LD (r2 ≥ 0.6) with cerebrospinal fluid biomarker levels. (C) In 17q24.2, we observed shared genetic influences between the overall macular thickness (right eye, overall_macular_thickness_right, index variant rs4791212) and the mean MO of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFO_MO, index variant rs12451721, PPH4 = 0.963). We also observed genetic overlaps (LD r2 ≥ 0.6) with self-reported math ability, risk-taking tendency, and loneliness. (D) In 11q13.3, we observed shared genetic influences between the ninth PC of the Vgg19 model on fundus image (Vgg19_PC9) and the functional connectivity within the auditory network (Auditory<=>Auditory, shared index variant rs12807936, PPH4 = 0.994).