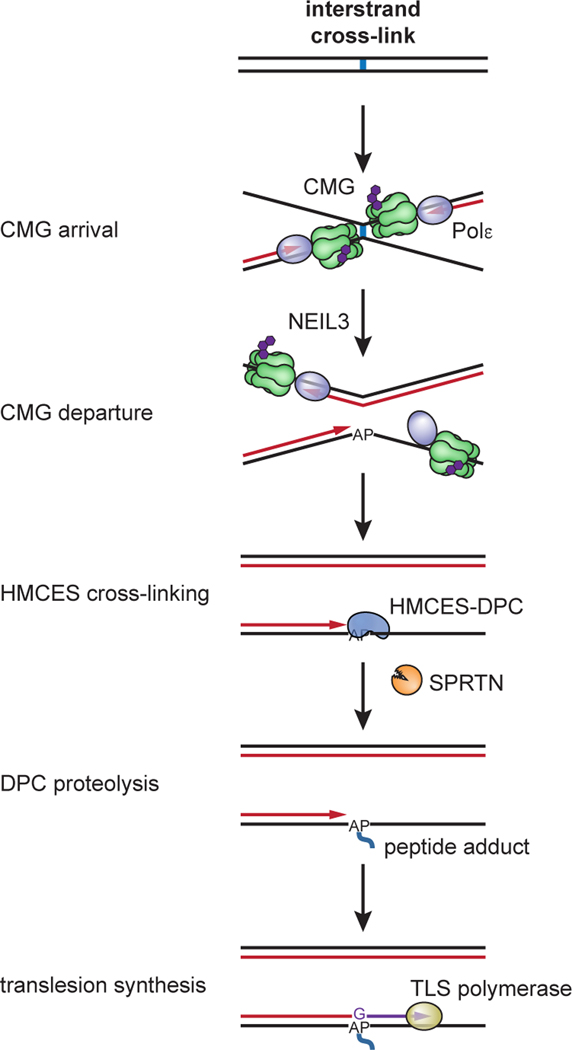
Fig. 7: Model for AP site protection by HMCES during NEIL3-dependent ICL repair.
Fork convergence at an ICL activates NEIL3-dependent unhooking and introduces an AP site in the leading strand template. The AP site is bypassed by CMG but stalls DNA polymerase, resulting in uncoupling of DNA unwinding from leading strand synthesis by Polε. This exposes the AP site at a ssDNA/dsDNA junction, where it is cross-linked by HMCES. The ssDNA/dsDNA junction abutting the HMCES-DPC activates proteolysis by SPRTN, but the resulting peptide adduct continues to stabilize the AP site until the lesion is bypassed by TLS. HMCES-DPC formation introduces a bias for dG insertion opposite the AP site.