Figure 1.
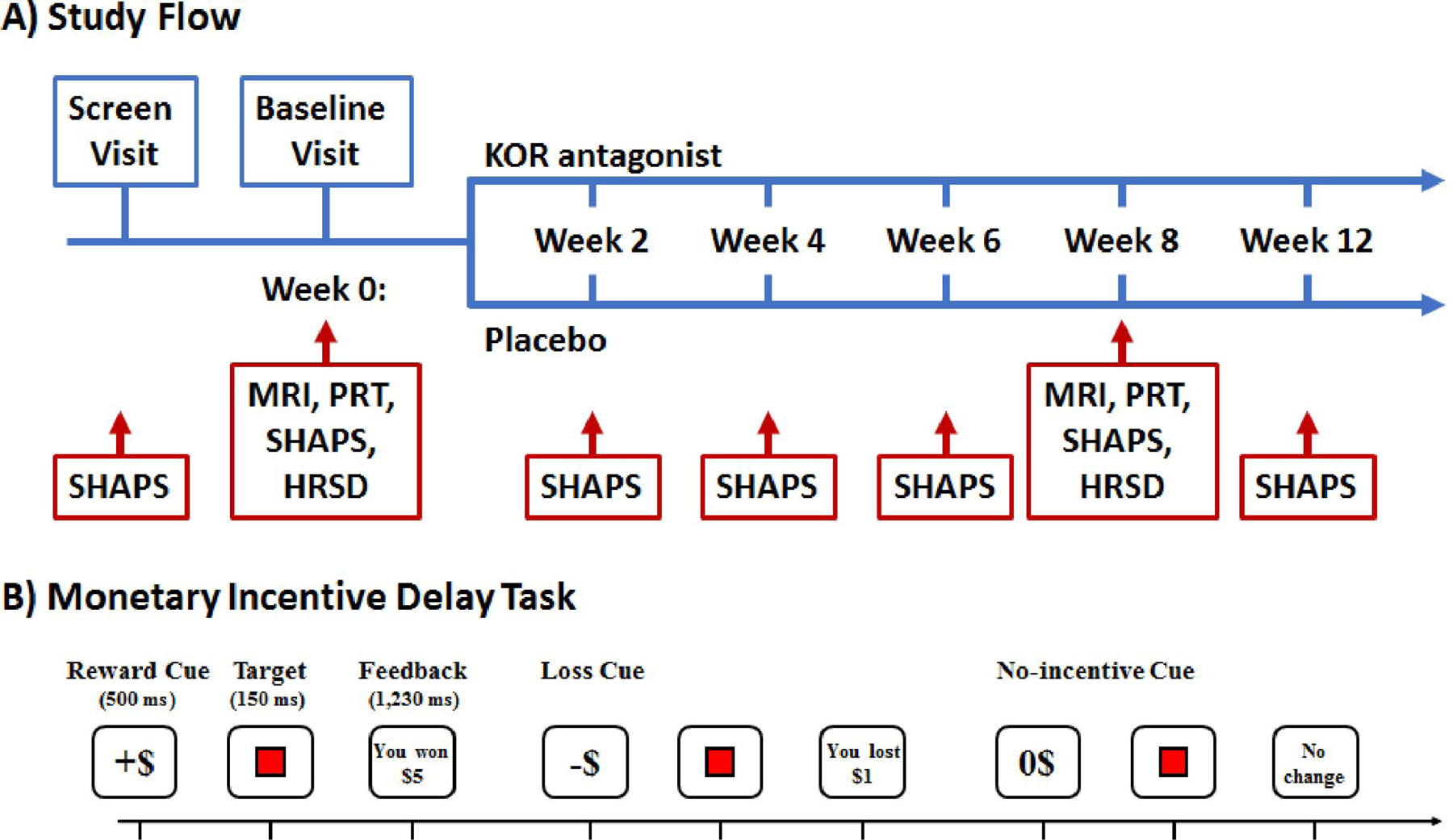
(A) Summary of Study Flow. Within 30 days following screening patients returned for a baseline visit, which included administration of the Snaith-Hamilton Pleasure Scale (SHAPS)28–31, which assesses anhedonic symptoms, Hamilton Depression and Anxiety Rating Scales32–33, MRI, EEG, and the Probabilistic Reward Task (PRT)34–40. Patients were then randomized to JNJ-67953964 (10 mg) or placebo (1:1 ratio) for eight weeks. After 8 weeks of double-blind treatment, patients underwent MRI, EEG, PRT, SHAPS and anxiety and depression scales and treatment was discontinued. At the final visit (week 12), patients were assessed for possible adverse effects. The primary outcome measure was ventral striatal activation during reward anticipation assessed with fMRI during the Monetary Incentive Delay (MID) Task.41–51 Secondary measures were the SHAPS and response bias in the PRT. The PRT is a computerized task that objectively measures participants’ ability to modulate behavior as a function of reinforcement history.34
(B) Trial Structure of the Monetary Incentive Delay (MID) Task. During fMRI, participants performed four runs of the MID (24 trials/run). For each trial (6 s), participants were presented with one of 3 possible cue shapes for 500 ms which signaled whether the upcoming trial had the potential for monetary gain (n=40; denoted by +$), potential for monetary losses (n=40; denoted by −$), or were no-incentive trials (n=40; denoted by 0$). Trial types were pseudo-randomly ordered within each run. After 2250–3750 ms, a red square target was presented for 150 ms. Participants were instructed that: for reward trials, they could win money if they responded quickly to the target; for penalty trials, they could avoid losing money if they responded quickly to the target; and for no-incentive trials there would be no monetary change, but they should still respond quickly to the target. Subjects received feedback 2400–3900 ms following target presentation. To standardize task difficulty, the 66th percentile of reaction times collected during a practice session was used to determine wins/penalties.
