Extended Data Fig. 8. cGAS and TLR3 cooperate to activate IRF3 signaling.
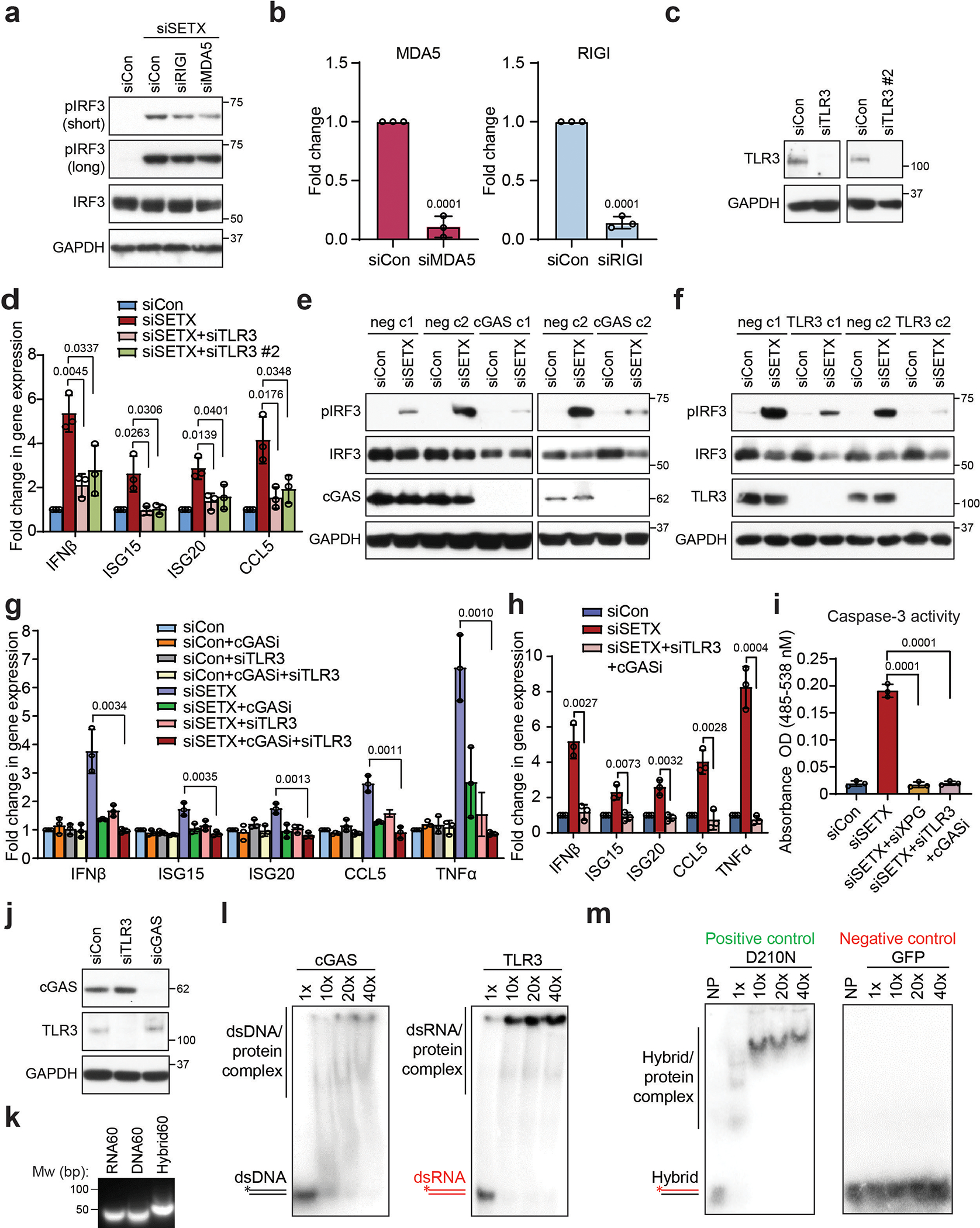
(a) Western blot showing pIRF3 levels upon siRNA-mediated knockdown of SETX and either RIG1 or MDA5 in HeLa cells. GAPDH is the loading control.
(b) RT-qPCR showing the knockdown efficiency of RIGI and MDA5 in HeLa cells.
(c) Western blot showing the knockdown efficiency of two different TLR3 siRNAs in HeLa cells.
(d) RT-qPCR measurements of IRF3 effectors upon TLR3 knockdown with two different siRNAs in siSETX-treated BAX−/−BAK−/− HeLa cells.
(e) and (f) Western blot showing levels of pIRF3 in two negative control (neg) clones and either cGAS knockout clones (e) or TLR3 knockout clones (f) generated using the CRISPR–Cas9 system in HeLa cells. c1 = clone 1, c2 = clone 2. GAPDH serves as the loading control.
(g) RT-qPCR measurements of IRF3 effectors upon single or combined inhibition/knockdown of cGAS and TLR3 in control and siSETX-treated HeLa cells.
(h) As in (g) but in BAX−/−BAK−/− HeLa cells.
(i) Caspase 3 activity assay after knockdown of SETX and either XPG knockdown or the combination of cGAS inhibition and TLRs knockdown.
(j) cGAS and TLR3 protein levels upon siRNA-mediated knockdown of TLR3 or cGAS in HeLa cells.
(k) Agarose gel showing DNA (60 nt) and RNA (60 nt) oligonucleotides can anneal to form a DNA/RNA hybrid.
(l) Gel shift assays of cGAS binding to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) (left) and TLR3 binding to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) (right).
(m) Gel shift assays show binding of human RNaseH1 D210N catalytically-inactive mutant and GFP protein to RNA-DNA hybrids which are used as positive and negative controls, respectively. NP stands for no protein.
Bar graphs are mean ± s.d.from three independent biological replicates (n = 3) (unpaired two-tailed t-test with CI = 95%). P values are shown at the top of the graphs.
