Extended Data Fig. 9. cGAS and TLR3 bind directly to cytoplasmic RNA-DNA hybrids.
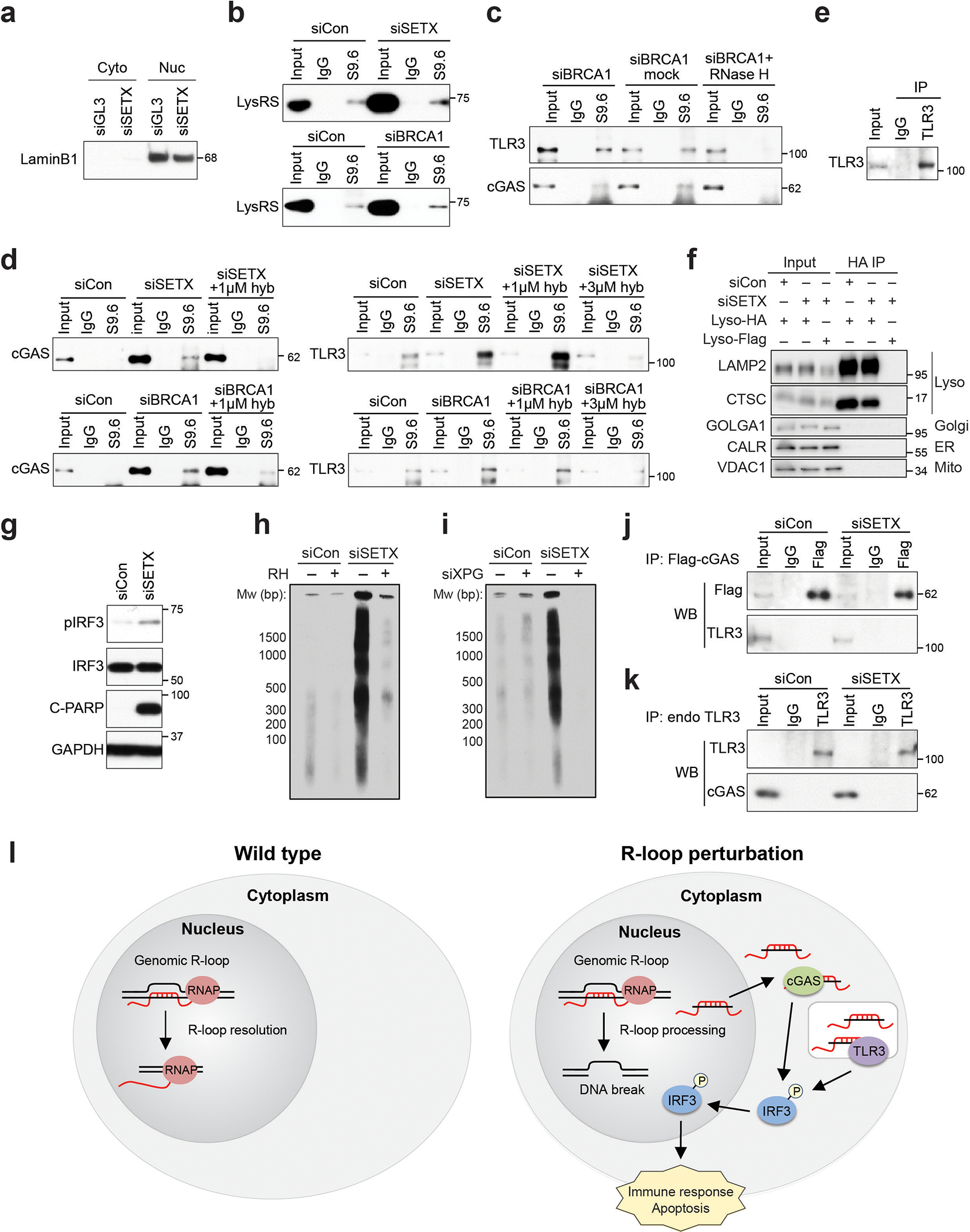
(a) The purity of the cytoplasmic fraction used for the S9.6 co-IP was assessed by western blot.
(b) S9.6 co-IP from the cytoplasmic fraction showing LysRS binds to cytoplasmic hybrids in our methods. LysRS has been reported to interact with cytoplasmic hybrids and serves as the positive control.
(c) S9.6 co-IP from the cytoplasmic fraction showing cGAS and TLR3 associate with RNA-DNA hybrids isolated from siBRCA1-treated cells, as well as the impact of 37°C no enzyme mock control and in vitro RNase H treatment before the IP step. RNase H treatment, 50 U/ml for 1 h at 37°C.
(d) S9.6 co-IP from cytoplasmic fraction showing cGAS binding to hybrids induced by siSETX is disrupted by 1 μM hybrid competitor in IP reaction, and TLR3 binding to hybrids is disrupted by 3 μM hybrid competitor in an IP reaction. hyb = hybrid.
(e) Western blot validating the TLR3 IP efficiency in experiments to detect TLR3-associated cytoplasmic hybrids by performing TLR3 IP followed by S9.6 IP (Fig. 4h).
(f) Western blot assessing the purity of the endolysosomal fraction after isolation following HA immunoprecipitation in control or SETX-depleted HA-TMEM192 HEK293T cells. Flag-TMEM192 HEK293T cells were used as a negative control for the LysoIP. Proteins marking the lysosome (Lyso), Golgi apparatus (Golgi), endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria (Mito) are indicated.
(g) Western blot showing pIRF3 and C-PARP levels induced by SETX knockdown in HA-TMEM192 HEK293T cells, as was observed in HeLa cells. This result suggests this cell line is suitable for the study of R-loop-induced immune activation. This experiment is a control for the LysoIP (Fig. 4i).
(h) cytoDRIP blot showing cytoplasmic hybrids levels are elevated upon knockdown of SETX in HA-TMEM192 HEK293T cells. In vitro RNase H digestion was used to ensure IP specificity. This experiment is also a control for the LysoIP.
(i) cytoDRIP blot showing cytoplasmic hybrids upon knockdown of SETX in HA-TMEM192 HEK293T cells with or without knockdown of XPG.
(j) co-IP testing the interaction between Flag-tagged cGAS and endogenous TLR3.
(k) co-IP testing the interaction between endogenous TLR3 and cGAS.
(l) Working model. Left: in wild-type cells, nuclear R-loops are efficiently resolved by RNase H or RNA-DNA helicases, such as SETX. Only a small number of R-loops are processed by XPG and converted to cytoplasmic hybrids, so that cytoplasmic hybrid levels are below the threshold required for activation of IRF3 signaling. Right: under certain perturbations, including depletion of SETX/BRCA1, or under pathological conditions that deregulate R-loops, a subset of nuclear R-loops that may not be efficiently resolved are processed by XPG, leading to RNA-DNA hybrid accumulation in the cytoplasm. These hybrids are then recognized by cGAS and TLR3 in the cytosol and endolysosome, activating IRF3-mediated immune signaling and apoptosis.
