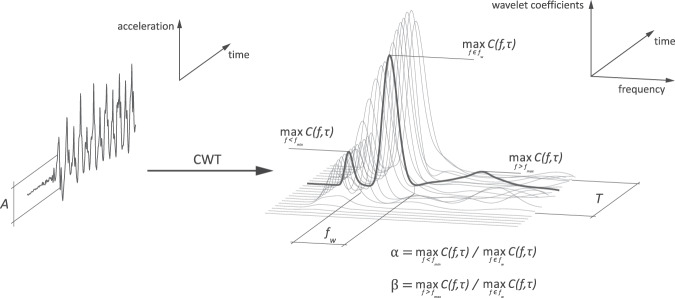
Fig. 2. Visualization of signal features.
Vector magnitudes of raw time-domain accelerometer signal is used to compute peak-to-peak amplitudes in one-second segments, which are then compared to a predefined threshold A; segments with amplitude below the threshold are excluded from further processing. Time-frequency decomposition computed using CWT reveals temporal gait features (wavelet coefficients) within, below, and above typical step frequency range , used to calculate gait harmonics parameters α and β. The activity is classified as walking when all amplitude- and frequency-based conditions are satisfied for at least T segments (seconds).