FIGURE 5.
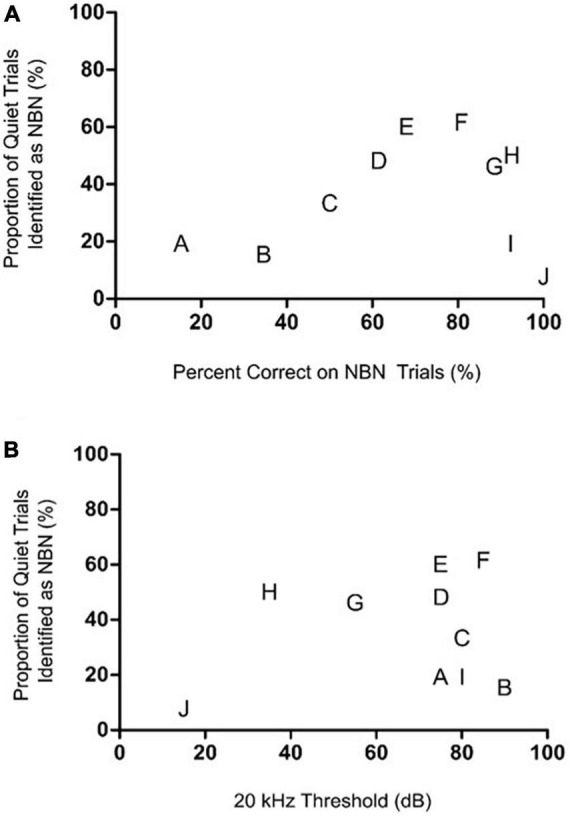
The rats’ degree of high frequency hearing loss or their ability to detect the steady NBN failed to predict their Quiet trial performance during the chronic tinnitus assessment. (A) Relationship between NBN and Quiet trial performance post-sound exposure during the chronic tinnitus assessment. When each rat’s post-sound exposure performance on NBN trials was plotted versus their Quiet trial performance, no correlation was observed, demonstrating that a rat’s Quiet trial performance was independent of its NBN trial performance [r(8) = 0.42, p > 0.05]. (B) Relationship between the post-sound exposure 20 kHz hearing threshold and Quiet trial performance during the screening for chronic sound-induced tinnitus. No correlation was observed between hearing thresholds at 20 kHz post-sound exposure and performance on Quiet trials [r(8) = 0.28, p > 0.05]. In both graphs, each rat is identified by a separate letter which corresponds to its designation in Figure 4, as this allows for visual comparisons to be made across these correlative analyses and the sham versus sound exposure results in Figure 4.
