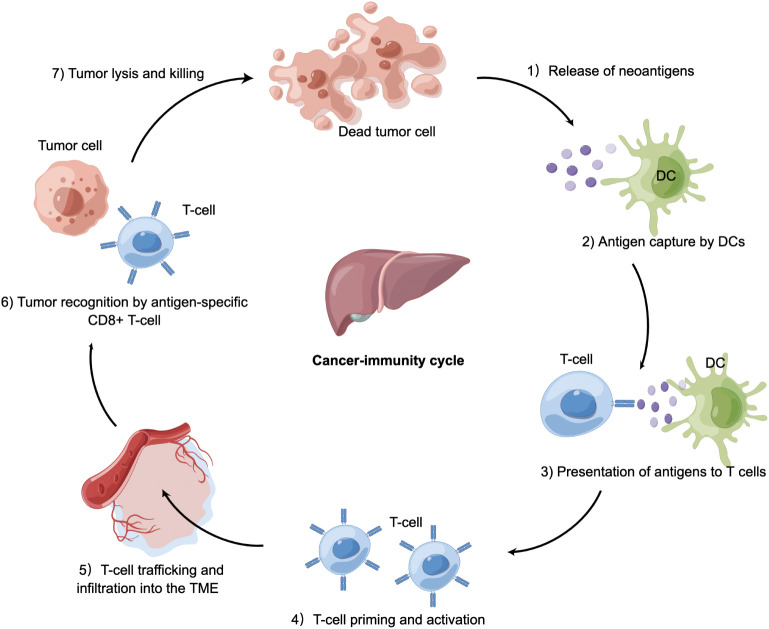
Figure 2.
Cancer-immunity in HCC. Tumor cells release antigens into the tumor microenvironment due to necrosis or treatment. Dendritic cells capture cancer antigens and traffic to the lymphoid organs where they present antigens to T cells, followed by T-cell priming and activation. These activated T cells migrate and infiltrate into HCC tissue. CD8+ T cells recognize HCC cells via T cell receptor. The final step is T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells, allowing more cancer-specific antigens to release. Tumor can perturb the processes mentioned above to occur immune evasion. DC, dendritic cell; TME, tumor microenvironment; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.