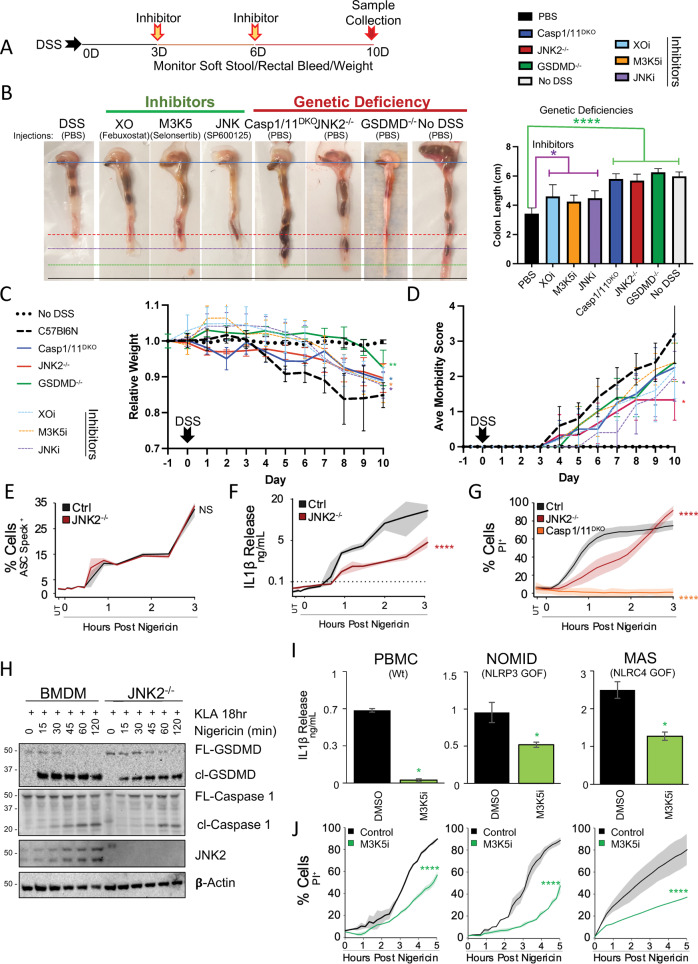
Fig. 7. XO:MAP3K5:JNK2 Pyroptotic Signaling is Required for DSS-induced Colitis in Mice and Supports Inflammatory Responses in Human Inflammasomopathies.
A–D Mice injected intraperitoneally with inhibitors (XO [febuxostat 30 mg/kg], JNK [SP600125 30 mg/kg], or MAP3K5 [selonsertib 30 mg/kg]) according to the treatment regimen (A), or the indicated knockouts, were assessed for susceptibility to 2% DSS-induced colitis via monitoring colon shortening (B), weight loss (C), and morbidity score from stool condition (D). E–G BMDM were assessed for ASC specking (E), IL-1β release (F), and PI uptake (G), following 18 h 100 nM KLA priming and a 10 µM nigericin trigger. H Jnk2−/− BMDM were primed for 18 h with 100 nM KLA and triggered with 10 µM nigericin to assess activatory cleavage of Caspase 1 (p20) and Gsdmd (cl-Gsdmd) via western blot. I–J Human PBMC from patients harboring gain-of-function mutations in various inflammasomes (NOMID: NLRP3 and MAS: NLRC4) were assessed for IL-1β release (I) and PI uptake (J) following extended priming −/+ 1 h 30 µM M3K5 inhibitor selonsertib and 10 µM nigericin triggering. A, B, D Data are represented as the mean of five mice (B–D), sample quadruplicates (E–G), or duplicate wells (I, J) per group while error bars (B–D, I) and shading (E–G, J) represent standard deviation from the mean. B, I Pair-wise two-tailed student’s T test of unequal variance; *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001. C–G, J Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test; ****p < 0.0001. A–J Data shown are representative of two (A–D, I, J) or three (E–H) experiments.