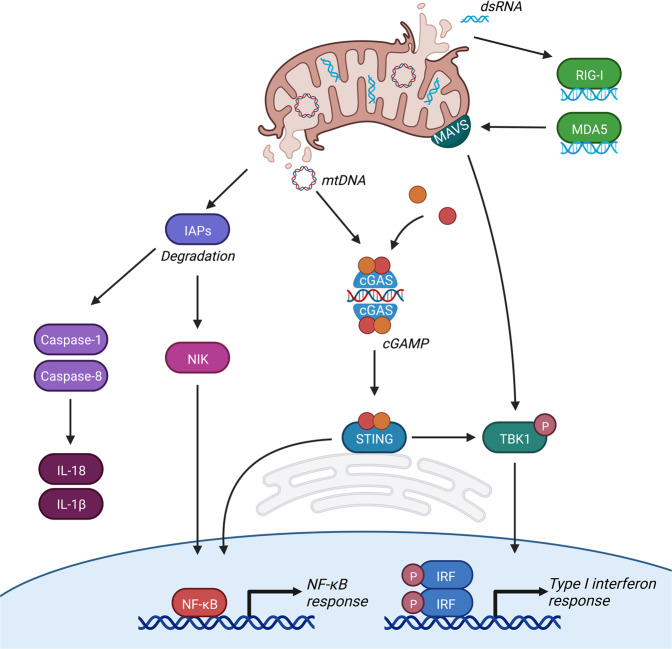
Fig. 3. MOMP-induced inflammation.
MOMP activates several pro-inflammatory pathways. (1) Under caspase-inhibited conditions MOMP causes IAP degradation which subsequently leads to NIK stabilisation and accumulation followed by the transcription of NF-κB target genes. In addition, degradation of IAPs activates caspase-1 and caspase-8 leading to processing and release of IL-1β and IL-18. (2) Cytosolic release of mtDNA leads to recognition of cGAS which subsequently forms cGAMP out of GTP and ATP. cGAMP is a second messenger for ER-resident STING initiating its activating and the subsequent transcription of NF-κB target genes and type I interferons. (3) Release of cytosolic dsRNA leads to its recognition by RIG-I and MDA5, followed by activation of mitochondria-localised MAVS and a type I interferon response.