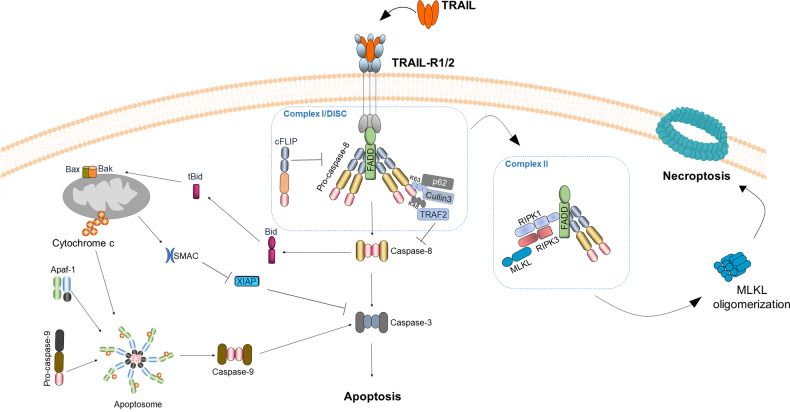
Fig. 1. TRAIL-induced cell death signaling pathways.
TRAIL-mediated death receptor trimerization enables the recruitment of FADD, which in turn binds to procaspase-8 to form the DISC. TRAIL-Rs, FADD and caspase-8 appear to exist in a 3:1:9 (Receptor:FADD:Caspase) stoichiometry [143]. cFLIP isoforms differentially control TRAIL signaling. Caspase-8 oligomerization and activation can be facilitated by the E3-ligases Cullin-3 which mediates K48/K63 ubiquitination of caspase-8 and subsequent recruitment of the Ub-binding protein p62 to the DISC, allowing p62-mediated aggregation and full activation of the caspase-8caspase-8 [144]. Following ubiquitination of caspase-8, TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) interacts with caspase-8 at the DISC, down-stream of Cullin3 and it is required for K48-linked polyubiquitination on the large catalytic domain of caspase-8, hence, triggering the proteasomal degradation of this protease and serving as a shut-off timer for the death ligand-mediated apoptosis [145]. In type I cells, DISC-activated caspase-8 is sufficient to activate caspease-3 and trigger apoptosis by the extrinsic pathway. In type II cells full activation of caspase-3 is inhibited by XIAP and therefore activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway is essential for full activation of caspease-3. Caspase-8 mediated activation of tBid triggers Bax and Bak to execute mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). MOMP results in the release of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC), thereby enabling the full activation of caspase-3. Additionally, cytochrome c is also released from the mitochondria and along with adaptor protein apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) forms the apoptosome which activates caspase-9, to enable amplification of caspase-3 activation and apoptosis. Upon TRAIL stimulation, following DISC assembly, a secondary cytoplasmatic complex can be formed, known as complex II, which retains the DISC components FADD, caspase-8 and RIPK1. In absence of caspase-8 or when its activity is blocked, RIPK1 recruits RIPK3, which in turn phosphorylates MLKL. Phosphorylated MLKL then oligomerises, which results in the execution of necroptosis.