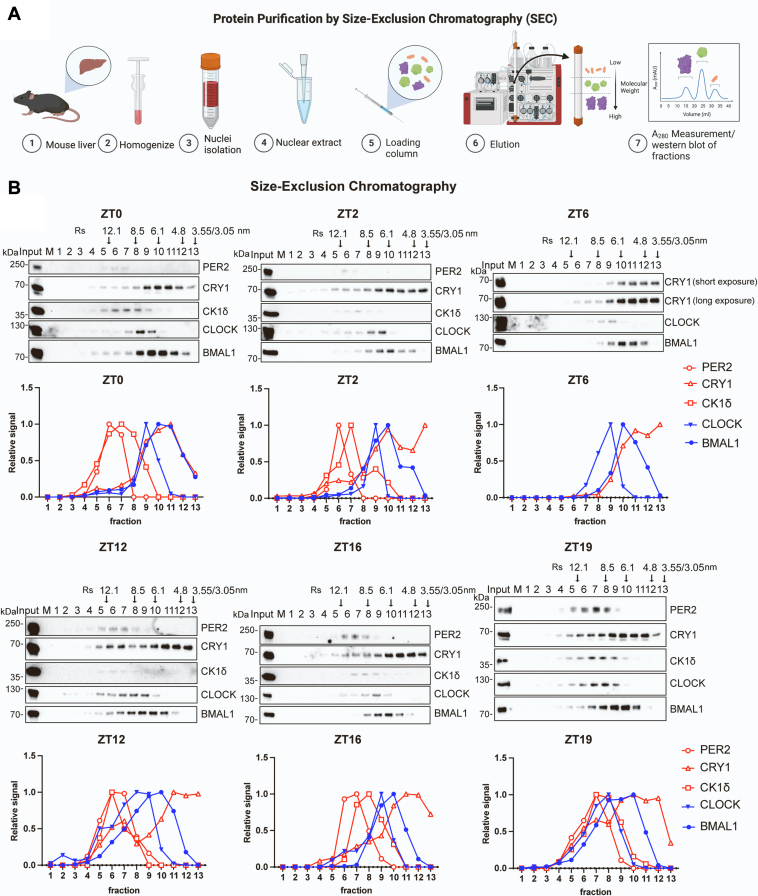
Figure 2.
Analysis of nuclear circadian complexes by gel filtration chromatography.A, method: Extracts were prepared as done for glycerol gradient analysis. Proteins in 50 to 90 ul of extract were separated using a Superose 6 Increase 10/300GL column. The column was standardized as shown in Fig. S2 using ovalbumin (45 kDa, Rs 4.8 nm), bovine serum albumin (66.5 kDa, Rs 3.55 nm), rabbit muscle aldolase (160 kDa, Rs 4.8 nm), horse spleen ferritin (440 kDa, Rs 6.1 nm), bovine thyroglobulin (669 kDa, 8.5 nm), IgM (990 kDa,12.1 nm), and Dextran (marker for void volume). B, elution profiles for PER2, CRY1, CK1δ, CLOCK, and BMAL1 determined for extracts of mice harvested at ZT0, ZT2, ZT6, ZT12, ZT16, and ZT19. For each ZT, the Western blot is above the graph showing quantitative values for band intensity of each protein relative to each protein’s peak intensity, given a value of 1. Arrows indicate positions of the peak elution fraction for each reference protein. Chromatographic analysis was done at least twice for each ZT, and representative images are shown.