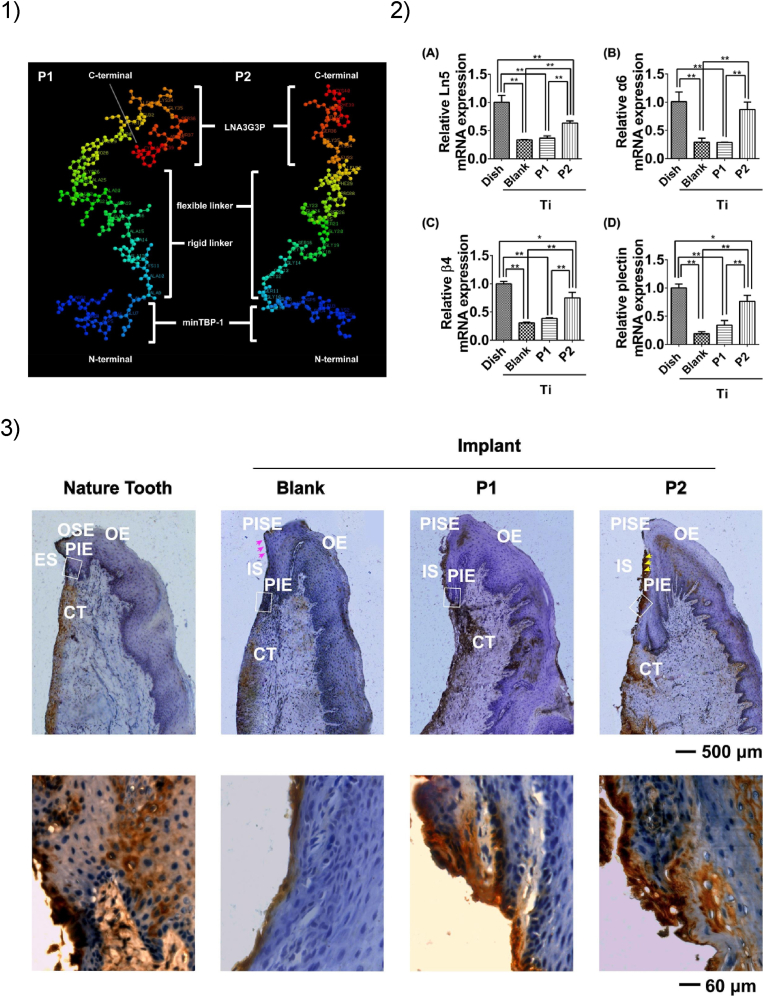
Fig. 7.
Example of a Ti-binding peptide used for the functionalization of dental titanium implants. 1) Pseudo-3D representation of fusion peptides P1 and P2. While the blue fragment at the N-terminal bins to the Ti surface, the peptide at the C-terminal binds to oral epithelial cells and activates soft tissue sealing around the implant. 2) Relative mRNA expression levels of Ln-5, Integrin α6, Integrin β4, and Plectin genes in human oral epithelial cells. The cells were cultured for 10 days on a culturing dish, uncoated titanium surfaces (bare) and peptide-coated titanium surfaces (P1 and P2). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that P2 strongly upregulates the expression of key genes involved in soft tissue sealing. 3) Immunohistochemical analysis of Ln-5 distribution. In the top row, the images show the gingival mucosa around the tooth and around implanted titanium abutments, either blank or coated with P1 and P2 peptides. The bottom row shows a magnification of selected areas (white square) indicated in the images above. For a complete interpretation of the figure, we refer the reader to the original publication. Reprinted from Ref. [296], with permission from Elsevier.