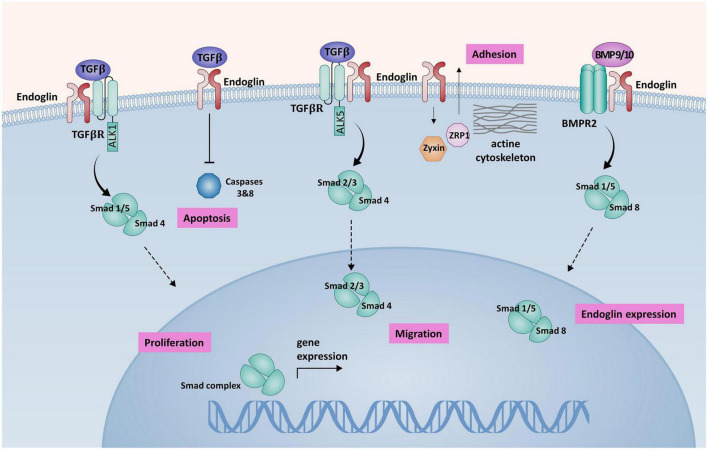
FIGURE 1.
A schematic presentation of endoglin-mediated signaling in endothelial cells (ECs). Endoglin associates with TGF-βRII and ALK1 forming a receptor complex, that binds TGF-β1. Activation of this receptor complex leads to the phosphorylation of Smad1/5 that form a complex with co-Smad (Smad4). Smad complex is then translocated to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of target genes, promoting cell proliferation. Association of endoglin with the ALK5/TGF-βII receptor complex inhibits Smad2/3 dependent signaling pathway, that has an antiproliferative effect on ECs. Endoglin promotes BMP9/10 signaling via BMPR2 receptor complex. Activation of BMPR2 receptor complex leads to Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation and subsequent increased endoglin expression in a positive feedback loop. Binding of TGF-β by endoglin induces inhibition of apoptosis via caspases 3 and 8 inhibition. Endoglin interaction with ZRP-1 and Zyxin regulates cell migration, inducing the reorganization of actin cytoskeleton and promoting cell adhesion (57).