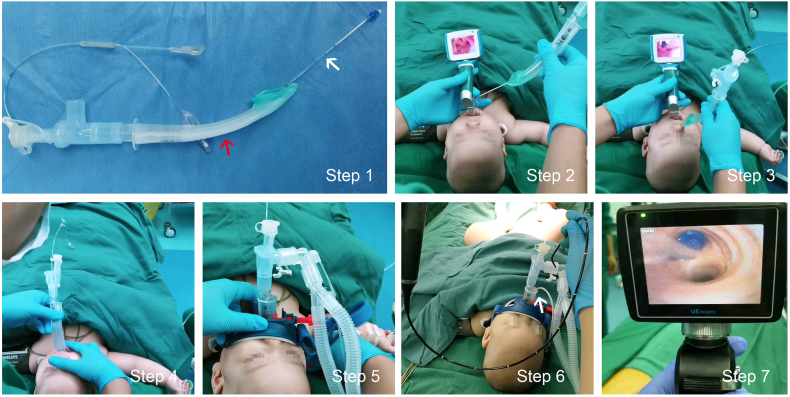
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the specific operation procedure of the combination of supraglottic airway and intraluminal placement of bronchial blocker.
Step 1: The BB (shown by the white arrow) well lubricated with paraffin oil traveled through the SGA ventilation tube (indicated by the red arrow) to form a combination; Step 2: The glottis was exposed through the visual laryngoscope and the previously formed combination was inserted into the trachea as a whole as in a regular endotracheal intubation operation; Step 3: The anterior cuff of the BB passed through the glottis with the SGA remaining outside the mouth; Step 4: The SGA was placed in the appropriate position of the pharyngeal cavity to ensure ventilation, leading the BB to theapproximate location of the tracheal carina; Step 5: A fixator was used to guarantee the position of the SGA; Step 6: A gastric tube of 8G highlighted by the white arrow was placed through the esophageal drainage tube of the SGA to lower intragastric pressure and thus reduce occurrence of reflux aspiration; Step 7: The 2.8-mm fiberoptic bronchoscope was inserted through the SGA and the depth of the BB was adjusted until the location was satisfactory reached under direct vision. Abbreviations: SGA, supraglottic airway; BB, bronchial blocker. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)