Figure 1.
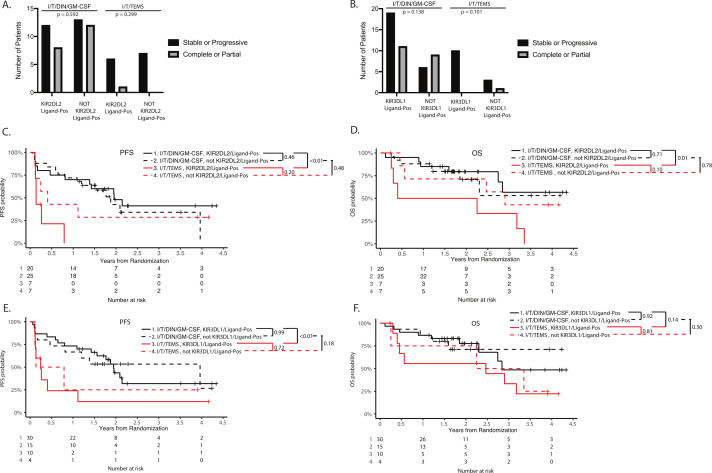
KIR/KIR ligand genotype and outcome. Neither KIR2DL2 with its ligand, nor KIR3DL1 with its ligand are associated with clinical outcome in patients receiving I/T/DIN/GM-CSF, however, these genotypes are associated with improved outcome when comparing I/T/DIN/GM-CSF versus I/T/TEMS. A, B) There were no significant differences in response rate based on KIR2DL2/ligand status (A) or KIR3DL1/ligand status (B). C, D) Patients positive for both KIR2DL2 and its ligand, HLA-C1 (KIR2DL2/Ligand-Pos), had significantly improved EFS (C) and OS (D) when treated with I/T/DIN/GM-CSF compared with those patients treated with I/T/TEMS (black solid line vs red solid line; EFS: p<0.01, OS: p=0.01). However, KIR2DL2/ligand-Pos status was not associated with outcome among patients treated with I/T/DIN/GM-CSF (EFS: p=0.46, OS: p=0.71). E, F) Similarly, those positive for both KIR3DL1 and its ligand, HLA-Bw4 (KIR3DL1/ligand-Pos), had significantly improved EFS (E), but there was no difference in OS (F) in patients treated with I/T/DIN/GM-CSF versus I/T/TEMS (black solid line vs red solid line; EFS: p<0.01, OS: p=0.14). Among patients treated with I/T/DIN/GM-CSF, KIR3DL1/ligand status was not associated with survival outcomes (black solid line vs black dashed line; EFS: p=0.18, OS: p=0.30). DIN, dinutuximab; EFS, event-free survival; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factory; I/T, irinotecan and temozolomide; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.