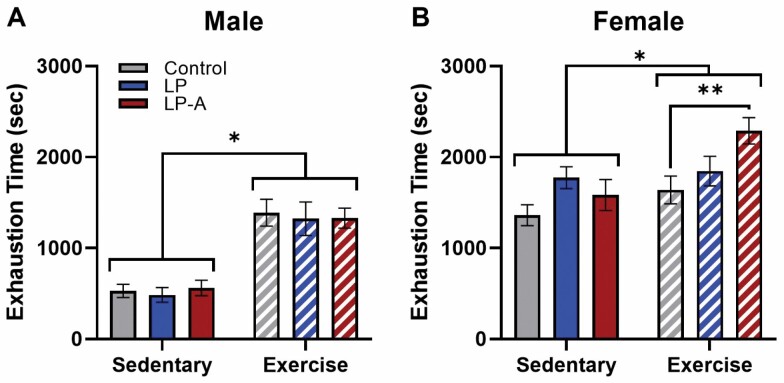
Figure 1.
Exercise tolerance in male and female rats. (A) While there was a significant main effect of exercise in male rats (p < .001), there were no significant effects of probiotic or subgroup interactions. (B) In female rats, there was both a significant main effect of exercise (p < .01) and probiotic group (p = .01). Moreover, there was a significantly longer time to exhaustion in the Ex-LPA group (p = .005). All data are expressed as group means ± 1 standard error of the mean. * indicates p < .05.