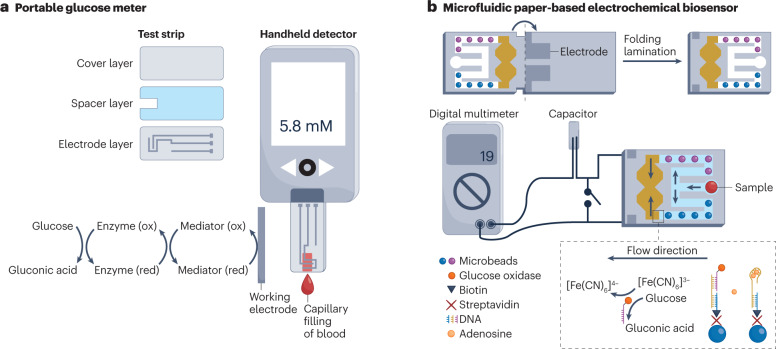
Fig. 2. Portable electrochemical biosensing devices.
a, Portable blood glucose meter consisting of a handheld electrochemical detector and disposable test strips. The test strip contains a bottom electrode layer, an adhesive spacer layer and a hydrophilic cover layer. The blood sample is introduced to the reaction chamber by capillary force. b, A paper-based microfluidic electrochemical biosensor for the detection of adenosine through aptamer-based affinity sensing. In one channel, adenosine is recognized by aptamer-functionalized microbeads (blue), resulting in the release of glucose oxidase-labelled DNA to catalyze the oxidation of glucose, which leads to the conversion of [Fe(CN)6]3− to [Fe(CN)6]4−. In the other channel, the microbeads are not functionalized (purple), allowing quantification of adenosine concentration. The current signal from the discharging of the capacitor is collected by a portable digital multimeter. ox, oxidation; red, reduction. Part b reprinted with permission from ref. 104, Wiley.