FIGURE 3.
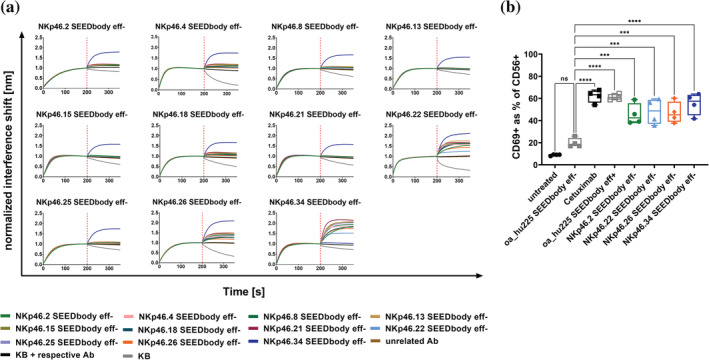
VHH‐based NKCEs target several distinct epitopes on NKp46 and trigger significant NK cell activation. (a) BLI sensograms showing competitive binding experiments of a panel of 11 NKp46 SEEDbodies for recombinant human NKp46 ECD. rhNKp46 ECD was immobilized to the sensor tip followed by a first association step using the respective SEEDbody at a concentration of 100 nM. Subsequently, a second association step was performed using another SEEDbody at 100 nM in the presence of 100 nM first analyte. In each experiment KB buffer as well as one SEEDbody in both association steps were included as controls. (b) Representation of CD69 expression for different NKCEs and control molecules within the CD56 positive NK cell population. Percentage of activation was determined by flow cytometric analysis via simultaneous NK cell staining with CD56 PE‐Cy7 and CD69 PE or respective isotype controls for appropriate gating adjustment (Figure S4). Graphs show box whiskers plots of four independent experiments measured in biological duplicates. ns, not significant; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 versus oa_hu225 SEEDbody eff−.
