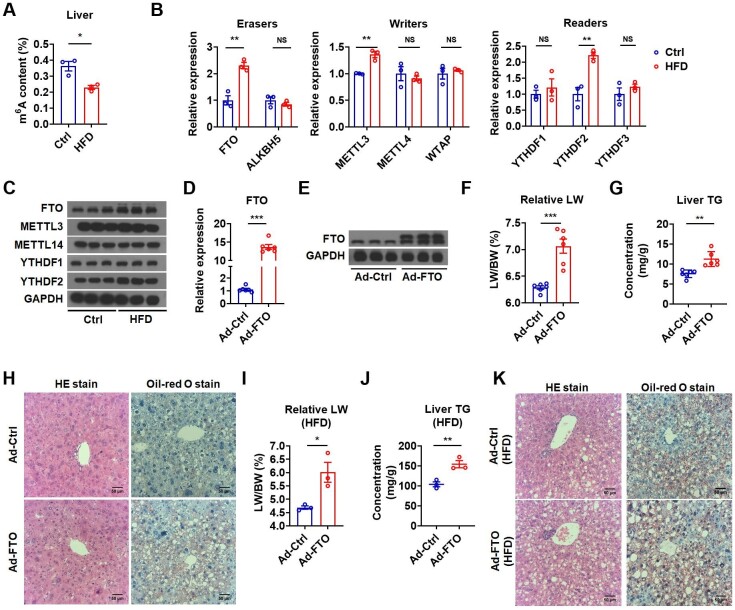
Figure 1.
Hepatic FTO is increased in HFD-fed mice and FTO overexpression facilitates hepatic TG accumulation. (A) The m6A amounts on total RNA in the liver of control and HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (B) Relative mRNA levels of demethylases (erasers), methyltransferase (writers), and methyl-specific binding proteins (readers) in the liver of control and HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (C) Protein levels of methyltransferase, demethylases, and methyl-specific binding proteins in the liver of control and HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (D) Relative mRNA levels of FTO in the liver of mice infected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO (n = 6). (E) Protein levels of FTO in the liver of mice infected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO (n = 3). (F and G) The ratio of liver weight to body weight (LW/BW, F) and liver TG contents (G) of mice injected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO (n = 6). (H) The representative HE and Oil-red O staining images in the liver of mice infected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO. Scale bar, 50 μm. (I and J) The LW/BW (I) and liver TG contents (J) of HFD-fed mice injected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO (n = 3). (K) The representative HE and Oil-red O staining images in the liver of HFD-fed mice infected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-FTO. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data shown are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. NS denotes not significant.