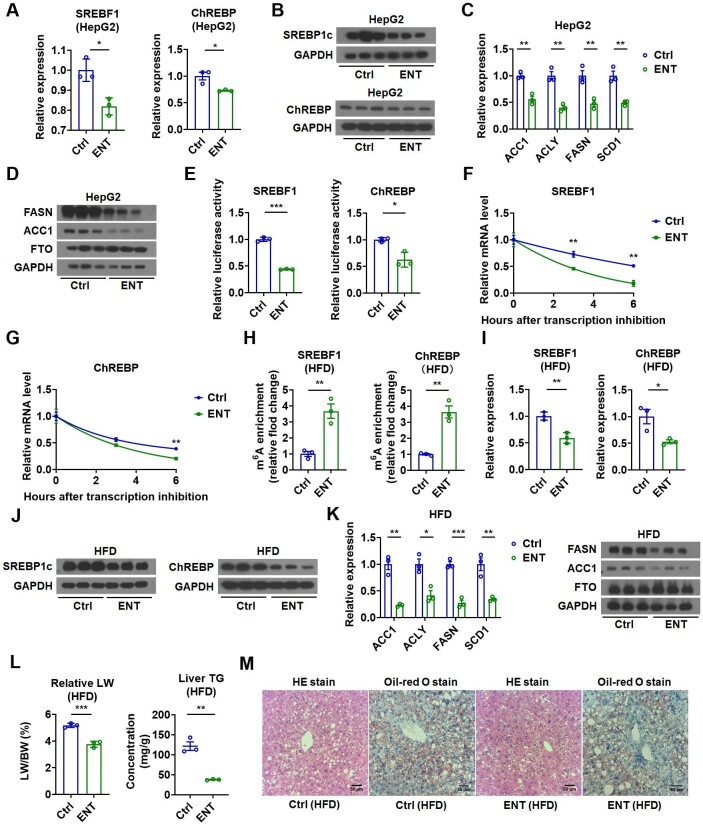
Figure 6.
FTO inhibition suppresses lipogenesis and prevents hepatic TG accumulation. (A) Relative mRNA levels of SREBF1 and ChREBP in ENT-treated HepG2 cells (n = 3). (B) Protein levels of SREBP1c and ChREBP in ENT-treated HepG2 cells (n = 3). (C and D) Relative mRNA levels of lipogenic genes and protein levels of FASN, ACC1, and FTO in ENT-treated HepG2 cells (n = 3). (E) Luciferase activity of the reporter containing the SREBF1 or ChREBP fragment with putative m6A sites after ENT treatment in HepG2 cells (n = 3). (F and G) The SREBF1 mRNA or ChREBP mRNA decay in ENT-treated Hepa1-6 cells (n = 3). (H) MeRIP analysis showing the increased enrichment of SREBF1 and ChREBP mRNAs in m6A-containing transcripts derived from the liver of ENT-treated HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (I) Relative mRNA levels of SREBF1 and ChREBP in the liver of ENT-treated HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (J) Protein levels of SREBP1c and ChREBP in the liver of ENT-treated HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (K) Relative mRNA levels of lipogenic genes and representative protein levels of FASN, ACC1, and FTO in the liver of ENT-treated HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (L) The LW/BW and liver TG contents in ENT-treated HFD-fed mice (n = 3). (M) The representative HE and Oil-red O staining images of the liver of ENT-treated HFD-fed mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data shown are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.