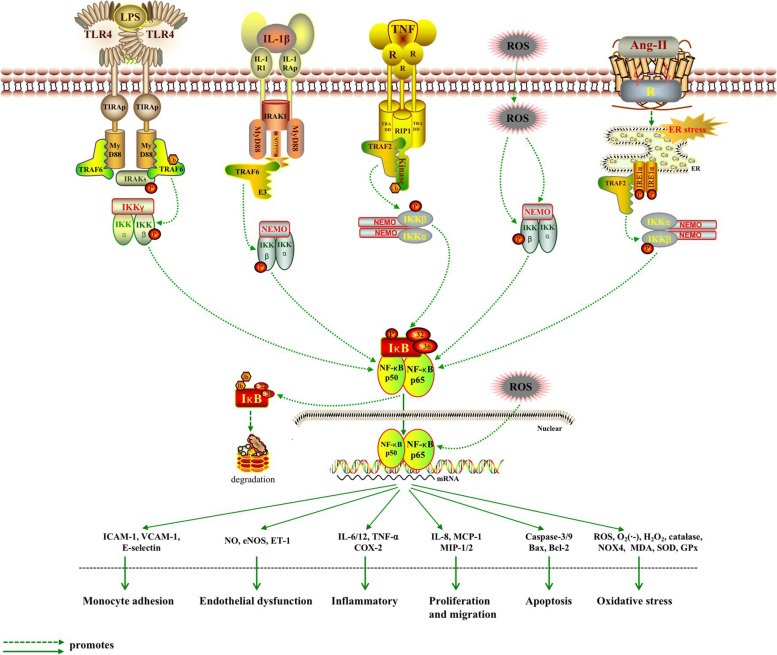
Fig. 2.
The Activation and regulation of IKKβ/NF-κB pathway. ①The binding of LPS to TLR4 recruits TIRAP. Then MyD88 joins the comlex which is bound by IRAKs and TRAF6 to activate IKKβ. ② MyD88 is recruited upon binds of IL-1 to IL-1RI. Then, IRAK1 comjoins the complex and TRAF6 also assemble to IKK complex. ③ The bingding of TNF with TNFR leads to the binding of TRADD, TRAF2 with the protein kinase RIP1, which forms a platform for the recruitment of TRAF2. When ubiquitinated RIP1 bindings to NEMO, it phosphorylates and activates IKKβ. ④ ROS from vascular lumen interact with various elements of the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway. On the other hand, the phosphorylation of p65 in which ROS are involved leads to a greater activation of NF-κB. ⑤ The binding of ang II induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activates and phosphorylates inositol-requiring 1α (IRE1α). Phosphorylated-IRE1α (p-IRE1α) recruits TRAF2, and then activates IKKβ. In the canonical pathway, IκBα is phosphorylated in an IKKβ- and NEMO(IKKγ)-dependent manner, which results in the nuclear translocation of mostly p65 or p50-containing heterodimers. Then, IκB degradates. The transcriptional p65 and p50 stimulate the production of inflammatory cytokines and finally monocyte adhesion, endothelial dysfunction, inflammatory, SMCs proliferation and migration, apoptosis, and oxidative stress all ensue. TIRAP: Toll/IL-1 receptor adaptor protein; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; TRAF6: TNF-R-associated factor 6; IRAKs: IL-1 receptor-associated kinases; TRADD: TNF-R-associated death domain; RIP1: receptor-interacting protein 1; TRAF2: TNF-R-associated factor 2