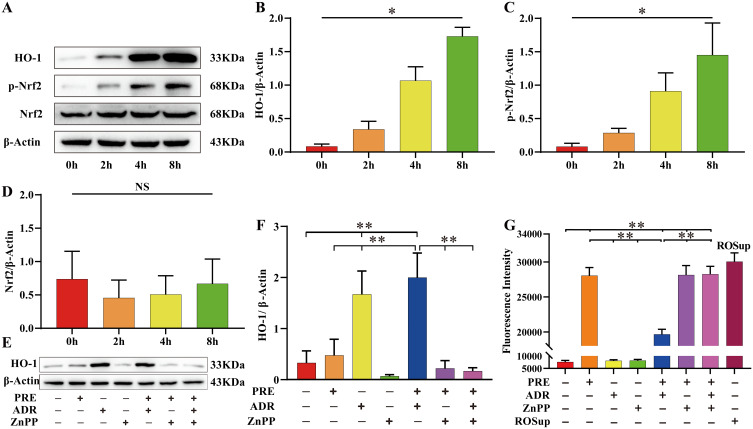
Figure 6.
ADR induced the expression of HO-1 in NPC to resist static mechanical pressure-induced damage. (A–D) Western blot was used to detect the effect of ADR on the expression of HO-1 and Nrf2. Total proteins were extracted from NPCs after various culture periods (0 h, 2 h, 4 h, and 8 h) using an ADR concentration of 10 µM and β-Actin as a reference. ADR induced the expression of HO-1 and p-Nrf2 in a time-dependent manner (P < 0.05) and had no significant effect on the expression of total Nrf2 (P > 0.05). Values measured are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n=3 for each group. (E–G) To clarify whether the cytoprotective effect of ADR was achieved by inducing the expression of HO-1, we used ADR or ZnPP to treat NPC for 8 h, followed by the application, or not, of 1.0 MPa static pressure for 24 h. The ROS content was significantly increased in the PRE group compared to the CTR group (P < 0.05). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, n=6 for each group. ADR promoted HO-1 expression and inhibited ROS accumulation in the ADR + PRE group compared to the PRE group (P < 0.05). The upregulation of HO-1 expression by ADR was reversed by ZnPP in the ADR + ZnPP + PRE group compared to the ADR + PRE group (P < 0.05), resulting in a significant increase in ROS (P < 0.05). Values measured are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n=3 for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Abbreviations: ADR, andrographolide; NPC, nucleus pulposus cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ZnPP, Zinc protoporphyrin (HO-1 inhibitor); CTR, control; PRE, pressure; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2; NS, non-significant.