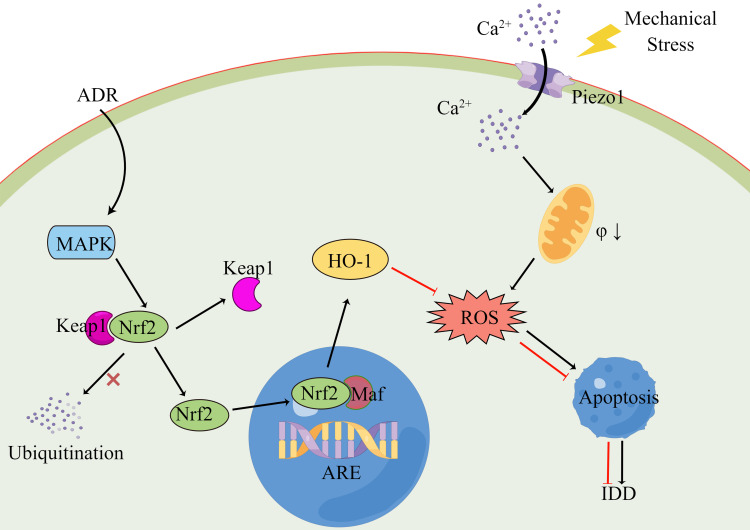
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of ADR inhibition of static mechanical pressure-induced apoptosis in NPCs. Mechanical stress can induce a change in the conformation of mechanically gated Piezo1 ion channels from a closed to an open state. The large inward flow of extracellular calcium ions decreases the potential difference between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes in the NPCs and causes damage to the mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondrial energy metabolism is disturbed and excessive ROSs are produced, exceeding the working capacity of the intracellular redox system, which eventually leads to apoptosis or cell death. ADR can activate the MAPK signaling pathway and inhibit the ubiquitination of Nrf2 by Keap1 to promote Nrf2 phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus and binding to ARE/EpRE. Ultimately, this induces the expression of antioxidant enzyme systems such as HO-1, inhibits intracellular ROS accumulation, improves NPC viability and inhibits apoptosis.
Abbreviations: ADR, andrographolide; NPC, nucleus pulposus cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1.