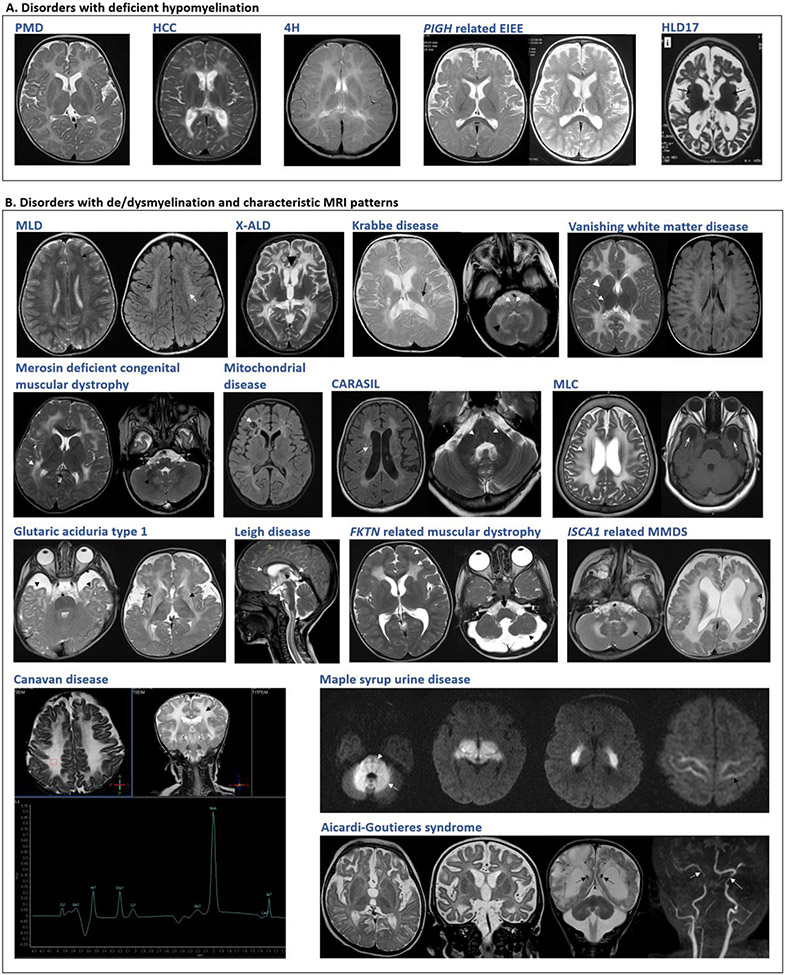
Figure 1. Neuroimaging findings in selected disorders.
A. Disorders with deficient myelination. Variable degrees of hypomyelination in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) at 11 months, hypomyelination with congenital cataract (HCC) at 5 years and 4H leukodystrophy (4H) at 5 years. Delayed myelination at 1 year in PIGH related early infantile epileptic encephalopathy which improved by 2 years. Advanced stage in hypomyelinating leukodystrophy type 17 showing cerebral, cerebellar atrophy. B. Disorders with de/dysmyelination and characteristic MRI patterns. Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD): T2W and FLAIR symmetrical white matter hyperintensity, sparing of subcortical U-fibers with tigroid pattern. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): T2W hyperintensities involving the white matter of bilateral parieto-temporal and frontal lobes. Krabbe disease: T2W hyperintense signals in the periventricular white matter, posterior limb of the internal capsule, brainstem along the pyramidal tracts and cerebellar white matter. Vanishing white matter disease: T2W hyperintensities and FLAIR hypointensities in deep and subcortical white matter, sparing basal ganglia and internal capsule. Merosin deficient congenital muscular dystrophy: T2W bilateral diffuse hyperintensities in deep cerebral white matter. Mitochondrial: Necrotizing leukoencephalopathy, FLAIR hyperintensity of bilateral white matter with cystic changes. Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL): FLAIR and T2W hyperintensities with lacunar infarcts and T2W hyperintensities indicating pons-arc sign. Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts (MLC): T2W hyperintensities with involvement of subcortical U-fibers. Subcortical cysts in anterior temporal lobes. Glutaric aciduria type 1: Temporal lobe hypoplasia, widened sylvian fissures and hyperintense basal ganglia with periventricular deep and subcortical white matter involvement. Leigh disease: Hyperintensities in corpus callosum, brain stem, spinal cord and thalamus. FKTN related dystroglycanopathy: Symmetric frontal lobar polymicrogyria-pachygyria complex, symmetrical changes in frontal lobe white matter. Brainstem and cerebellar hypoplasia seen. ISCA1 related multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome (MMDS) 5: Diffuse cerebellar and cerebral white matter hyperintensities, ventriculomegaly and pachygyria. Canavan disease: Diffuse bilateral symmetrical T2W white matter hyperintensity with subcortical U-fiber involvemen, Elevated NAA on MRS. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD): Diffusion-weighted images show symmetrical diffusion restriction in cerebellar white matter, brain stem, cerebral peduncles, posterior limb of internal capsule, thalami, and perirolandic cerebral white matter. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome: Delayed myelination, high signal in frontotemporal white matter with atrophy. SWI sequence shows calcifications, paucity of white matter, cerebellar atrophy and arteriopathy in advanced stage.