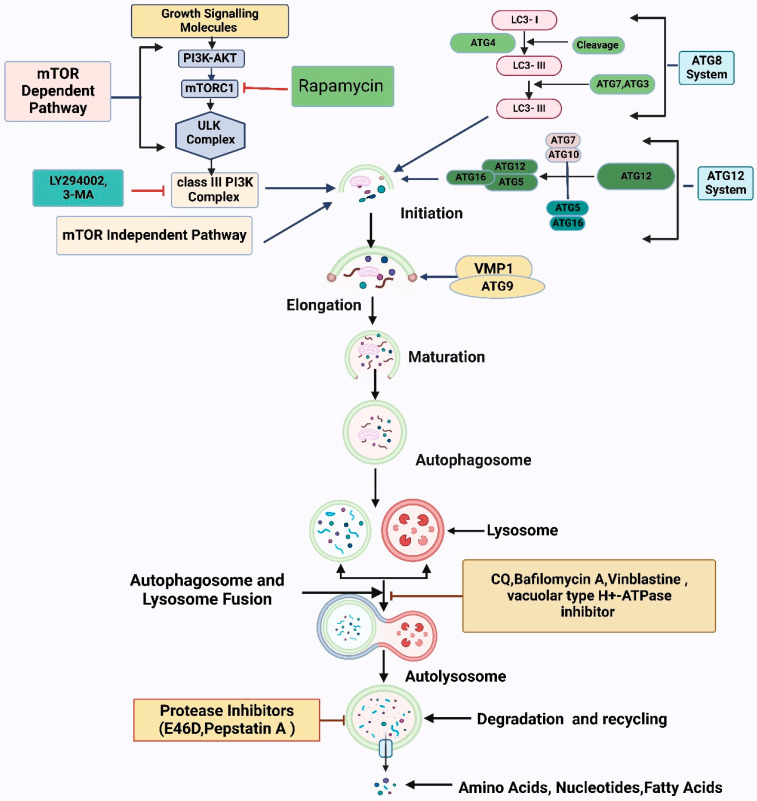
Figure 1.
The autophagy pathway’s biological role and its underlying molecular mechanism. The autophagy process starts when the action of several proteins creates a structure called a pre-autophagosome. The interaction of the ULK1/VPS34/beclin-1 complex impacts phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) to begin pre-autophagosome assembly. Additionally, the ATG5/ATG12/ATG16 and ATG12/ATG5/LC3 complexes are involved in causing phagophore nucleation and the accumulation of elongated macromolecules, in addition to their ability to bind to the developing autophagosomes. With the assistance of the ESCRT/SNARE/RAB7 protein complex, lysosomes can attach to mature autophagosomes, ultimately leading to autolysosome production. Finally, acid hydrolases successfully dismantle autolysosomes, liberating metabolites and nutrients.