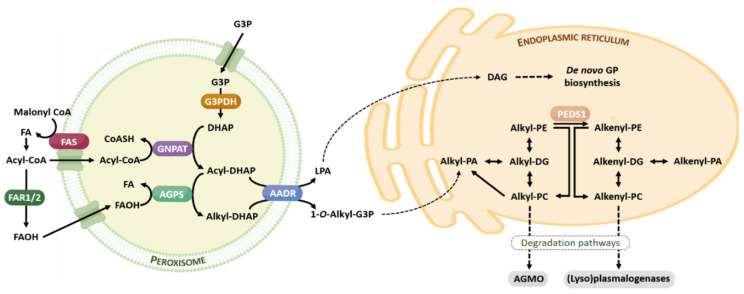
Figure 2.
Ether lipid metabolism. The ether lipid biosynthesis process initiates in peroxisomes and is subsequently completed in the endoplasmic reticulum. Briefly, the early steps of ether lipid biosynthesis in the peroxisomes are based on substrates derived from fatty acid metabolism (AcylCoA) and glycolysis (DHAP), and the rate-limiting step is the provision of FAOH. The completion of GP biosynthesis occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum using DAG and Alkyl-PA as precursor molecules. The catabolism of ether lipids proceeds by their lyso-forms for alkyl lipids, and is catalyzed by AGMO, and by (lyso)plasmalogenases in the case of alkenyl lipids. Abbreviations: AAG, alkyl-acylglycerol; AGMO, alkylglycerol monooxygenase; AGPS, alkylglycerone phosphate synthase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; FAOH, fatty alcohol, FAR 1 and FAR2, fatty acyl-CoA reductase; FAS, fatty acid synthase; G3P, glycerol 3-phosphate; G3PDH, glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GNPAT, glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase; GP, glycerophospholipid; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; PEDS1, plasmanylethanolamine desaturase. For additional details see references [19,20].