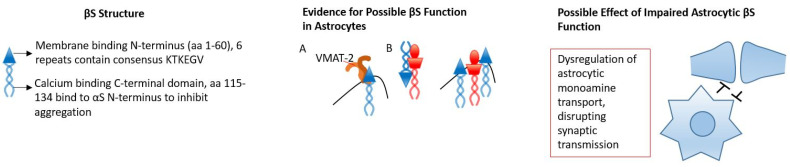
Figure 2.
βS only contains 6 repeated sequences with the consensus of KTKEGV in the N-terminus. βS’s calcium-binding C-terminus is also responsible for the inhibition of αS aggregation by interacting with the N-terminus of αS. In A, it has been shown in neurons that βS facilitates monoamine transport through VMAT-2, which would likely result in this function in astrocytes. In B, βS inhibits detrimental αS aggregation through two methods, the C-terminus region binding with the αS N-terminus to form heterodimers and inhibit aggregation, and βS competing with αS for membrane binding. The likely effect of impaired βS functioning in astrocytes would be dysregulation of astrocytic monoamine transport from the synapse and within the astrocyte for release.