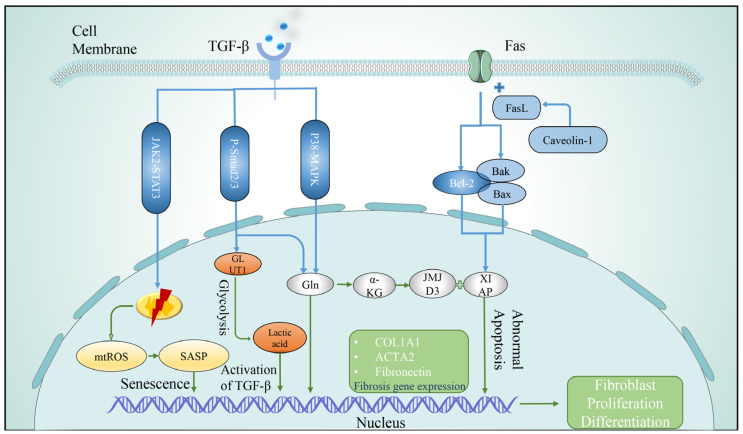
Figure 4.
Abnormal activation of fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The abnormal activation of fibroblasts in the pathological formation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis mainly involves the activation of TGF-β-related pathways JAK2-STAT3, pSmad2/3, and P38-MAPK. Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to increased reactive oxygen species, SASP formation, and cell senescence. Metabonomics such as abnormal metabolism of glucose and amino acids. Fas-FasL apoptosis pathway was inhibited, the expressions of pro-apoptotic proteins Bak and Bax were decreased, and the expressions of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and XIAP were increased. The above work together to promote fibroblast proliferation and differentiation and induce fibrosis. Abbreviations: TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; SASP, senescence-associated secretory phenotype; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GLUT1, glucose transporter 1; Gln, glutamine; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; JMJD3, jumonji domain-containing protein-3; XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis.