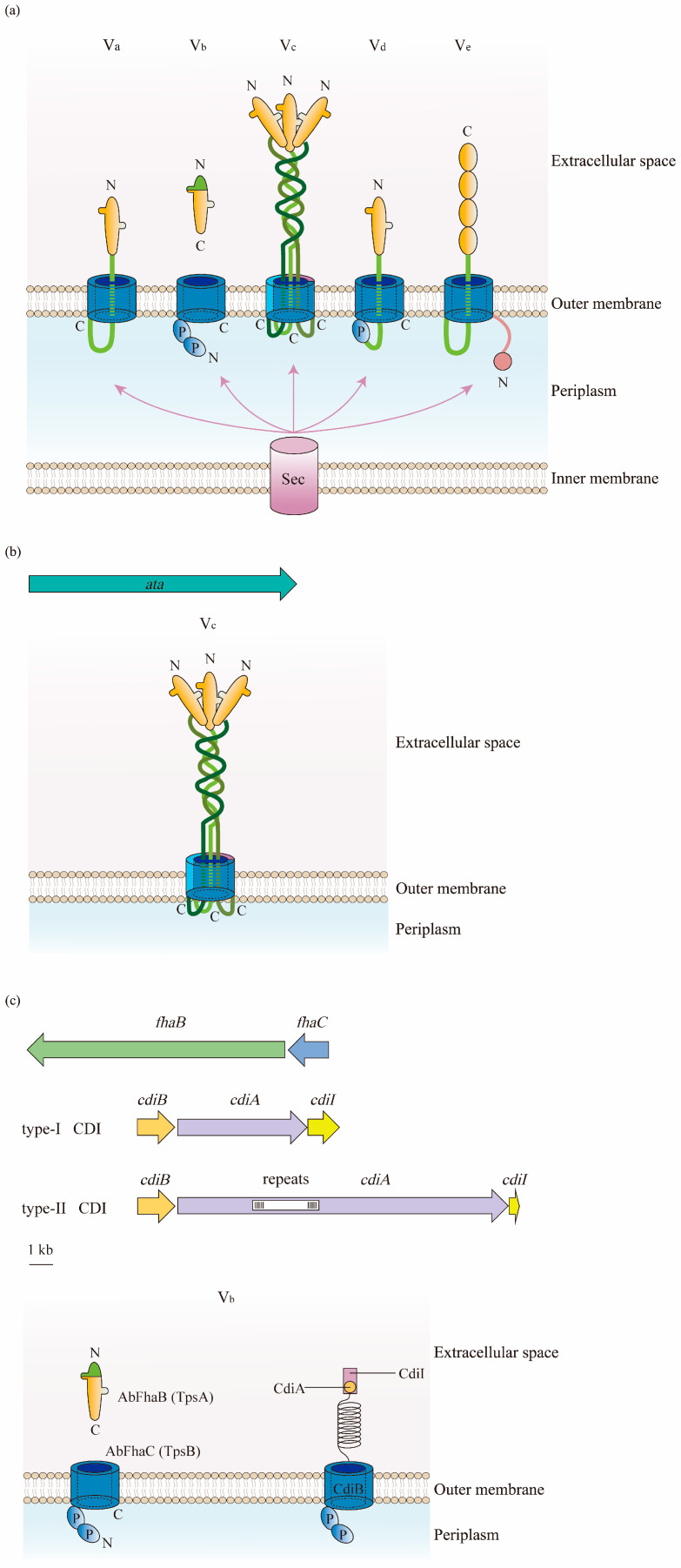
Figure 4.
Structure of the type V secretion system (T5SS) in A. baumannii: (a) There are five types of T5SS in Gram-negative bacteria. They consist of three parts: a signal sequence at the N-terminus, a secreted passenger in the extracellular milieu, and a transporter at the C-terminal. β-Barrels are displayed in blue; linkers and the two-partner secretion (TPS) domains are in green; passenger regions are in orange; polypeptide transport-associated (POTRA) domains are labeled as P; and the N- and C-termini are indicated. The translocation of substrates for subclasses of T5SS from the cytoplasm to the periplasm relies on the Sec pathway. (b) Type Vc is the most frequently identified T5SS in A. baumannii. It is formed by a trimeric protein, Ata, which contains a signal peptide at the N-terminus, a surface-exposed passenger domain, and a C-terminal domain. (c) Two forms of type Vb are found in A. baumannii. The one belonging to the TPSS is constructed of AbFhaB and AbFhaC, which represent TpsA and TpsB in other Gram-negative bacteria, respectively. AbFhaB (TpsA) is the passenger domain that is secreted out of cells through the outer membrane (OM) by AbFhaC (TpsB), which is the translocator domain located in the OM. Another one is the contact-dependent inhibition (CDI) system composed of CdiA and CdiB. Similar to TpsA, the toxin CdiA is released from the periplasm to the cell surface by the OM transporter CdiB.