Figure 1.
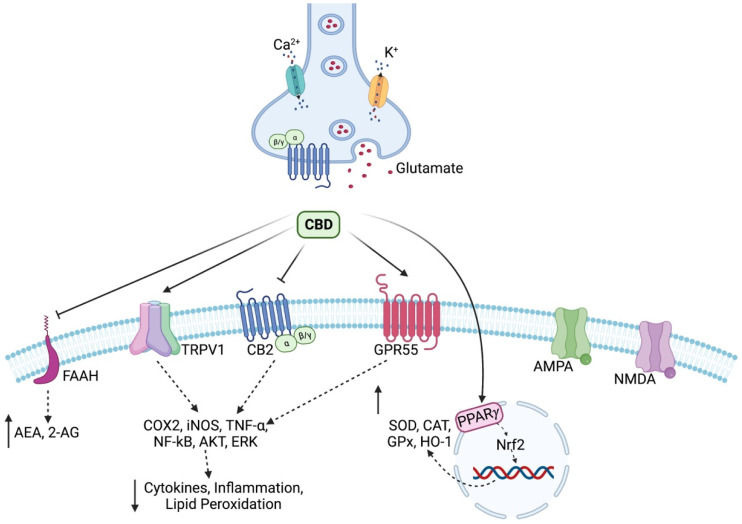
Cannabidiol has the property of inhibiting the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme with a consequent increase in the availability of anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), which are substances of the endocannabinoid system considered to be reverse mediators of depolarization-induced inhibition. Thus, it prevents the release of glutamate, which no longer acts on AMPA and NMDA receptors. At the same time, CBD, through TRPV1, GPR55, and CB2 receptors, prevents the generation of cytokines with a pro-inflammatory role, and in addition, through the PPARγ receptor, it increases the expression of endogenous antioxidant systems via the Nrf2 pathway. Created with BioRender.com.