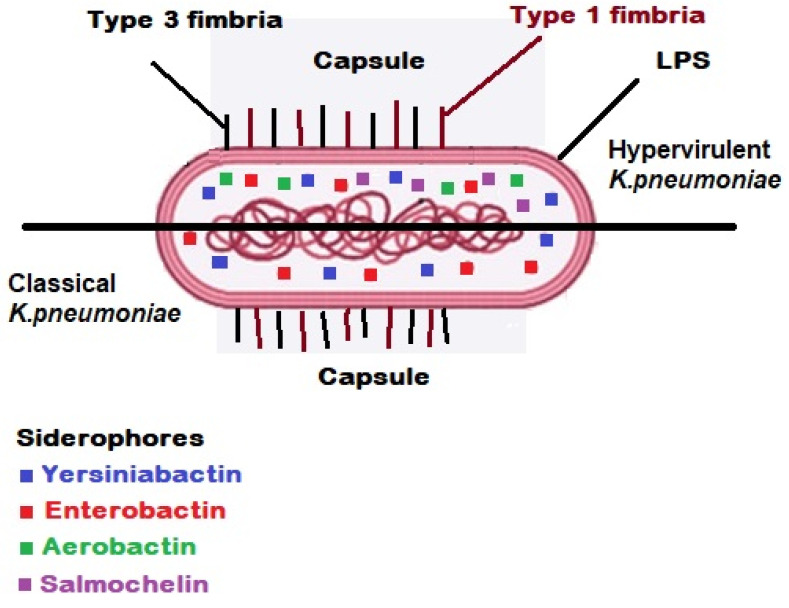
Figure 1.
Virulence factors in classical/hypervirulent strains of K. pneumoniae [57]. Two types of fimbriae are involved in pathogenesis of the bacteria through attachment to the biotic (human host urothelium) and abiotic (urinary catheter) surfaces to start the process of colonisation, biofilm formation and bacterial invasion. The polysaccharide capsule in K. pneumoniae is known as a pivotal virulence factor which acts as the outermost layer in a bacterial cell and interacts with the host. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an effective protective structure against serum complement proteins in parallel with the presence of capsule.