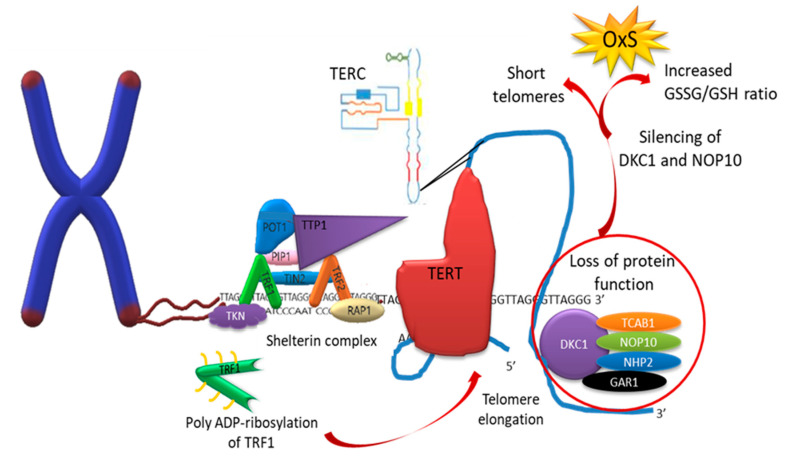
Figure 2.
Representation of the telomerase. Telomerase is a DNA polymerase responsible for extending the 3′-end of chromosomes. It is composed of TERT reverse transcriptase, TERC telomeric RNA, and associated proteins, including DCK1, NOP10, NHP2, and GAR1. The poly ADP-ribosylation of TRF1 stimulates telomere elongation, whereas a loss of function of the associated proteins can lead to telomere shortening. Silencing of DCK1 and NOP10 can also cause oxidative stress (OxS). Key components of sheltering and telomerase complex are described as follows: TRF1 (telomeric repeat-binding factor 1); TRF2 (telomeric repeat-binding factor 2); POT1 (protection of telomeres protein); PIP1 (POT1-interacting protein 1); TIN2 (TRF1-interacting nuclear factor 2); RAP1 (repressor activator protein 1); TERC (human telomerase RNA component); TCAB1 (telomerase Cajal body protein); NOP10 (H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 3); NHP2 (H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 2); GAR1 (H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 1); DCK1 (dyskerin); and TNKS (tankyrase protein).