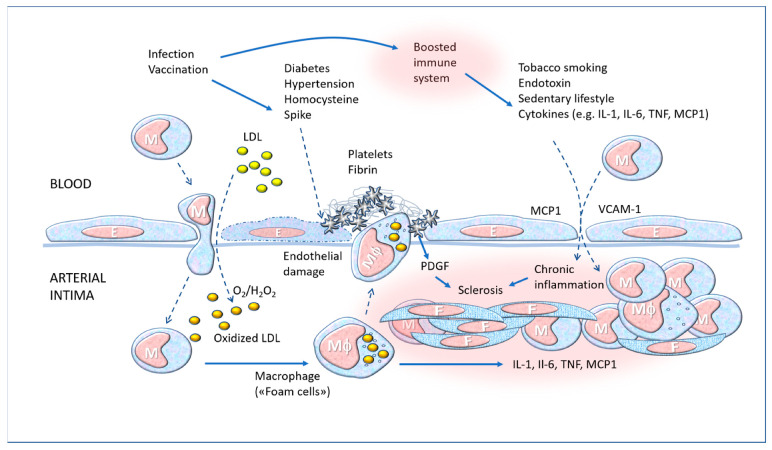
Figure 7.
Essential mechanisms of pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, seen as a chronic inflammatory disease. M: Monocyte; Mϕ: Macrophage; E: Endothelial cell; F: Fibroblast; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion protein 1; PDGF: platelet-derived growth factor; TNF: tumour necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; MCP1: Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 (CCL2). Solid line arrows: action, operation; dashed line arrows: moving, displacement.