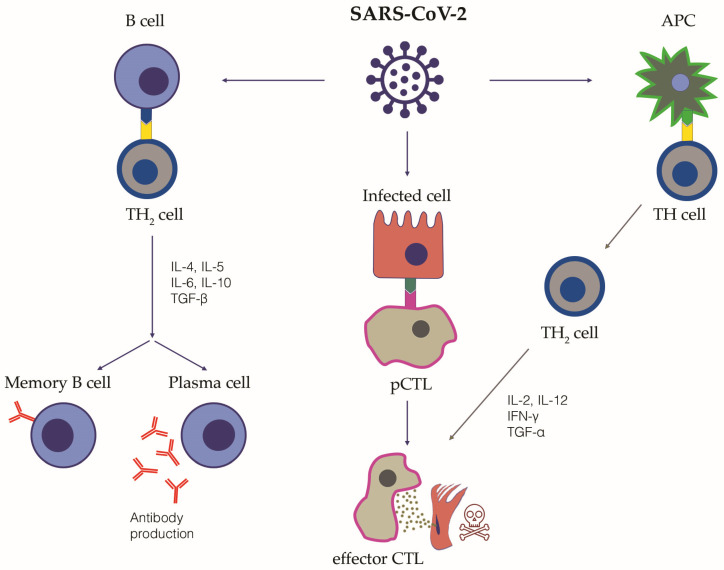
Figure 1.
The adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. This figure schematically summarizes the adaptive immune response following SARS-CoV-2 infection. The cellular pathways and the relative key cytokines are highlighted. Following their activation by interaction with the antigen-presenting cells (APC), TH2 lymphocytes are able to release cytokines and activate B cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), which exert their cytotoxicity on infected cells. Promoting CTL can also be directly activated by the interaction with SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Once activated, B cells can differentiate into plasma cells, releasing specific anti SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, and Memory B cells. The immunological memory towards SARS-CoV-2 is mediated both by virus-specific memory B lymphocytes, but also virus-specific memory CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, Natural Killer T lymphocytes and circulating antibodies. TH, T Helper cell; APC, antigen-presenting cell, CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor; IFN, interferon.