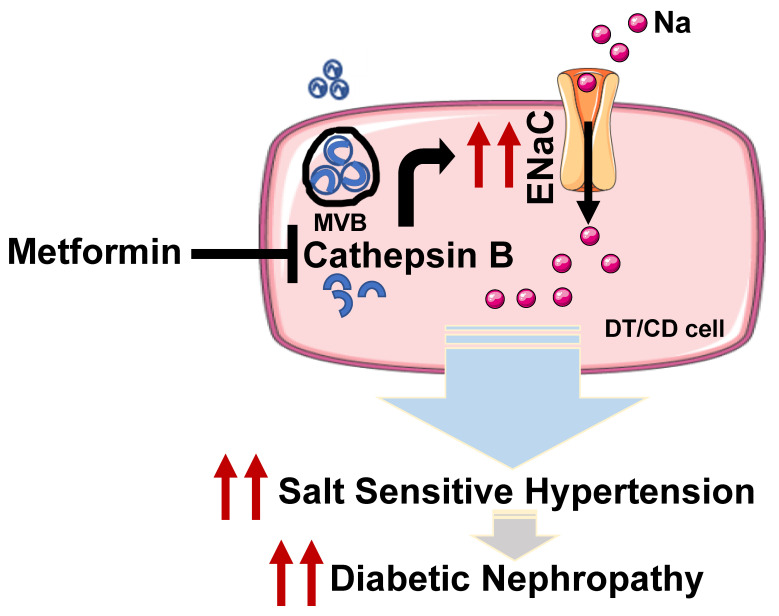
Figure 8.
Mechanistic model showing a putative role for metformin in inhibiting renal NCC and ENaC activation and reducing blood pressure in the diabetic kidney. An increase in cathepsin B mediated proteolysis of ENaC alpha in distal tubule (DT) and collecting duct (CD) cells, contributes to the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the diabetic kidney. Hypertension exacerbates the development of diabetic nephropathy. Metformin attenuates Cathepsin B levels in the kidneys and in EVs to alleviate salt-sensitive hypertension in the diabetic kidney. In addition, metformin reduces the density of ENaC at the luminal membrane. MVB refers to multivesicular body.