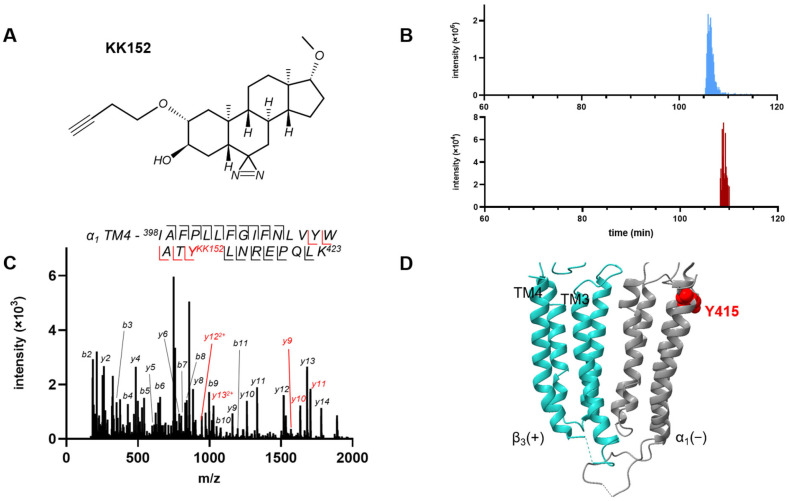
Figure 4.
Photolabeling of α1β3 GABAA receptors by KK152 (the enantiomer of KK123). (A) The structure of KK152. (B) Extracted ion chromatograms from mass spectrometric analysis illustrating the labeling of α1-TM4 peptide in α1β3 GABAA receptors by KK152. The y-axis shows the intensity of the unlabeled TM4 peptide (top panel) and the KK152-labeled TM4 peptide (bottom panel). The x-axis shows the chromatographic retention time of the unlabeled TM4 peptide (blue, 105.9 min) and the KK152-labeled TM4 peptide (red, 108.5 min) illustrating that the increased hydrophobicity of the labeled peptide lengthens retention time on reversed phase chromatography. (C) HCD fragmentation spectrum of the α1 subunit TM4 tryptic peptide photolabeled by 30 μM KK152. Red and black indicate fragment ions that do or do not contain KK152, respectively. The peptide sequence shows that the y-ion series of fragment ions contains diagnostic peptides indicating labeling of residue α1 (Y415). (D) Structure of the α1β3 GABAA receptor showing the location of Y415, the residue labeled by KK152 at the exoplasmic end of α1 TM4. The α1 subunit is shown in grey and the β3 subunit in turquoise.