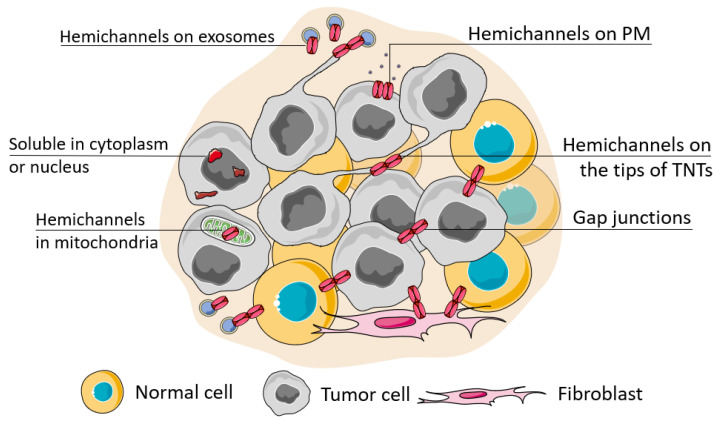
Figure 2.
Possible localization of connexins in the cell. The localization of connexins in the cell can be attributed to its soluble forms (located in the nucleus or cytoplasm) or membrane-bound forms which can be observed during its trafficking, ultimately represented as a functional connexin residing in the cell membrane in the hemichannel or channel state (when docked with a connexin of a neighboring cell). The localization of connexin channels at the membrane can be considered relatively to their localization to the basal membrane (cell polarity), attributed to cell protrusions (e.g., tunneling nanotubes, TNTs) or extracellular vesicles (e.g., exosomes). Connexins can be also transferred to the inner membrane of mitochondria.