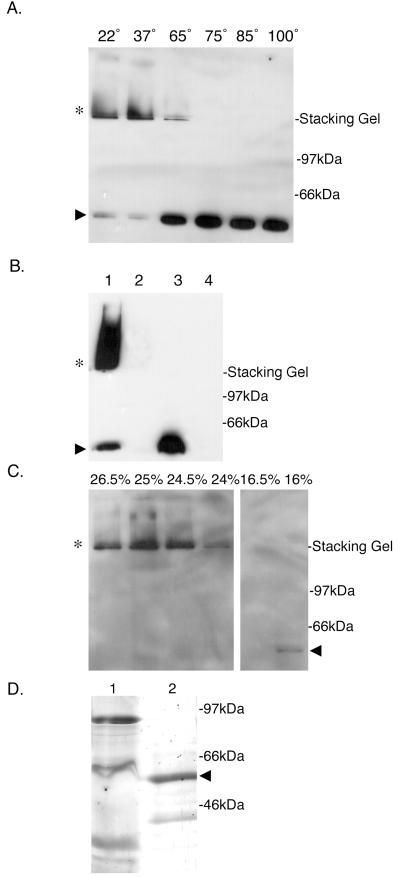
FIG. 1.
BfpB forms a HMW outer-membrane complex. (A) Temperature-dependent stability of the BfpB multimer in SDS. Purified outer membranes (3 μg of protein), prepared from the wild-type strain B171-8, were incubated in SDS-PAGE sample buffer at the indicated temperatures (in centrograde). Following SDS-PAGE, Western blot analysis with anti-BfpB antiserum was performed. When incubated in PAGE sample buffer at temperatures of 22 and 37°C, BfpB migrates principally as an HMW complex (∗) with some monomeric species (▸). At temperatures greater than 65°C, the predominant species is the monomer of BfpB (▸). (B) HMW complexes reactive with BfpB antisera (∗) are not detected in the bfpB deletion strain, B171-8ΔB2. Whole cells were sonicated and incubated in SDS-PAGE sample buffer for 7 min at the indicated temperature, and equal protein amounts were loaded onto a 12% polyacrylamide gel. Western blot analysis with anti-BfpB antiserum was performed. Lane 1, B171-8 whole-cell sonicate incubated at room temperature; lane 2, B171-8ΔB2 whole-cell sonicate incubated at room temperature; lane 3, B171-8 whole-cell sonicate incubated at 100°C; lane 4, B171-8ΔB2 whole-cell sonicate incubated at 100°C. (C) Isolation of the BfpB multimer by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Outer membranes isolated from B171-8 bacteria were solubilized at 37°C in a buffer containing 4% SDS and loaded onto a linear sucrose gradient. Following centrifugation, 20-μl aliquots from individual sucrose gradient fractions were mixed with an equal volume of SDS-PAGE sample buffer and loaded onto a 12% polyacrylamide gel without prior heating of the sample. Immunoblotting with anti-BfpB antiserum was used to detect BfpB. The BfpB HMW complex (∗) localized to 25% sucrose, while the BfpB monomer localized to 16% sucrose (◂). (D) Characterization of the isolated BfpB multimer. Sucrose gradient fractions containing the BfpB multimer were boiled in sample buffer and separated on a 12% polyacrylamide gel, and the proteins were visualized by silver staining. Lane 1, 30 μg of the outer-membrane starting material, heated for 7 min at 100°C in SDS-PAGE sample buffer; lane 2, 30 μg of sucrose gradient fractions containing the BfpB HMW complex, heated for 7 min at 100°C in SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The primary protein identified by silver staining corresponds to the size of the BfpB monomer (◂). Immunoblotting with anti-BfpB antiserum was used to confirm the identity of the two silver-stained bands and to conclude that the smaller 39-kDa band is a BfpB breakdown product. A band corresponding to BfpB cannot be detected in the crude outer-membrane fraction, most likely because it is a minor component of the outer membrane.