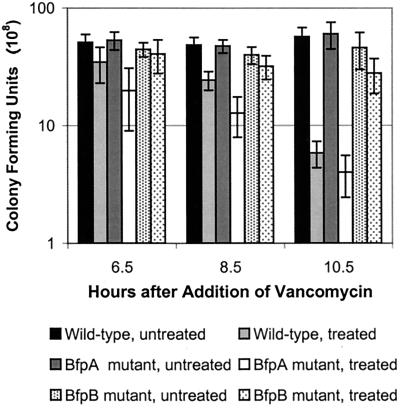
FIG. 7.
The BfpB complex renders cells susceptible to vancomycin. Vancomycin at a final concentration of 8 μg/ml was added to shaking DMEM cultures at 37°C, 1.5 h after inoculation from an overnight culture. Bacteria were collected from vancomycin-treated cultures and untreated control cultures, diluted, and plated 6.5, 8.5, and 10.5 h after addition of the antibiotic. Surviving colonies were counted the following day. Each data point on the graph is the average of at least six separate experiments, and error bars represent the standard deviations. The wild-type strain is B171-8, the BfpA mutant is B171-8ΔAcm, and the BfpB mutant is B171-8ΔB. B171-8 and B171-8ΔAcm, both of which express the outer-membrane BfpB multimer, were significantly killed by vancomycin 10.5 h after the addition of the antibiotic. By contrast, the viability of B171-8ΔB, which does not express the outer-membrane BfpB multimer, was not significantly affected by antibiotic addition.