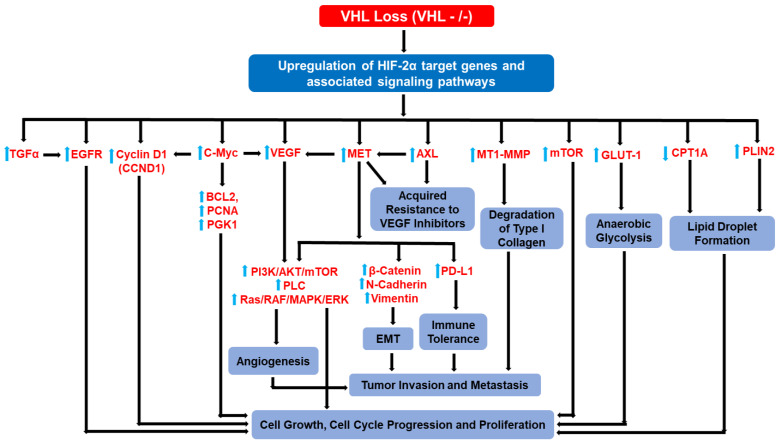
Figure 3.
HIF-2α-induced genetic responses and the associated oncogenic hierarchical events leading to ccRCC progression. HIF-2α induces the expression of multiple target genes (e.g., EGFR, CCND1, c-Myc, MET, VEGF, mTOR, GLUT1, CPTA1). Such gene reprogramming events promote angiogenesis, cell proliferation/growth, cell cycle progression, EMT, tumor migration/invasion, anaerobic glycolysis, lipid accumulation, immune tolerance, and drug resistance, which collectively lead to advanced ccRCC. Various functional interplay among target proteins and downstream pathogenic consequences are depicted above. VEGF-mediated tumor angiogenesis, for example, can promote tumor invasion and growth. Similarly, metabolic reprogramming (e.g., glycolysis induction) initiated by Glut1 can sustain cancer growth.