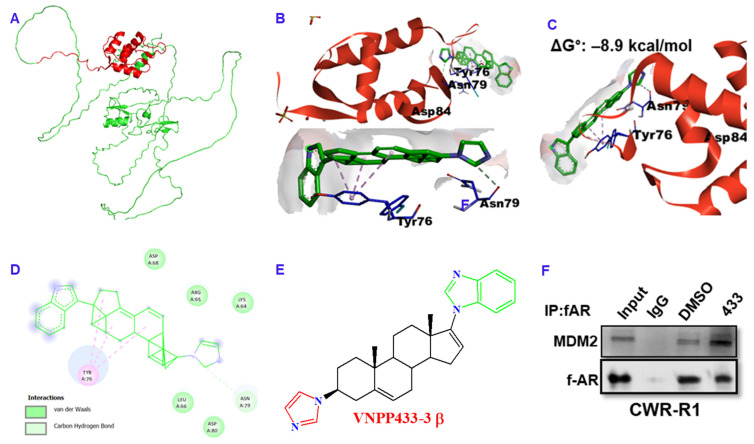
Figure 4.
VNPP433-3β acts as molecular glue that induces proximity in MDM2 and f-AR, facilitating MDM2-mediated ubiquitination of f-AR. (A) Predicted structure of full-length MDM2 (Alpha fold). Region in red represents amino terminal domain (amino acids 17–125) used for docking. (B) X-ray crystallographic structure of amino terminal domain (amino acids 17–125, PDB ID 2AXI) showing VNPP433-3β docked on protein surface with high affinity; ΔG°: –8.9 kcal/mol. (C) The ligand is bound to the surface of MDM2 primarily through the amino acids Tyr 76, Asn 79 and Asp 84, leaving a large portion of the ligand exposed and available to bind AR. (D) Major interactions (pi-alkyl with Tyr 76 and Carbon-Hydrogen boding with Asn 79) of VNPP433-3β with protein peripheral surface amino acids. (E) The 2D chemical structure of VNPP433-3β. (F) Co-immunoprecipitation of f-AR and MDM2 demonstrates that interaction of f-AR and MDM2 is enhanced in presence of VNPP433-3β. The CWR-R1 is an androgen-independent cell line derived from CWR22 tumors that expresses functional mutated AR (H874Y) and more accurately represent genetic composition of recurrent tumors than the immortalized DU145 or PC3 cell lines [28]. CWR-R1 cells were hormone-starved for 48 h and treated with DMSO or VNPP433-3β for 4 h. Cell lysate containing 1 mg protein was subjected to immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblotting for f-AR and MDM2. The uncropped blots are shown in Figure S2.