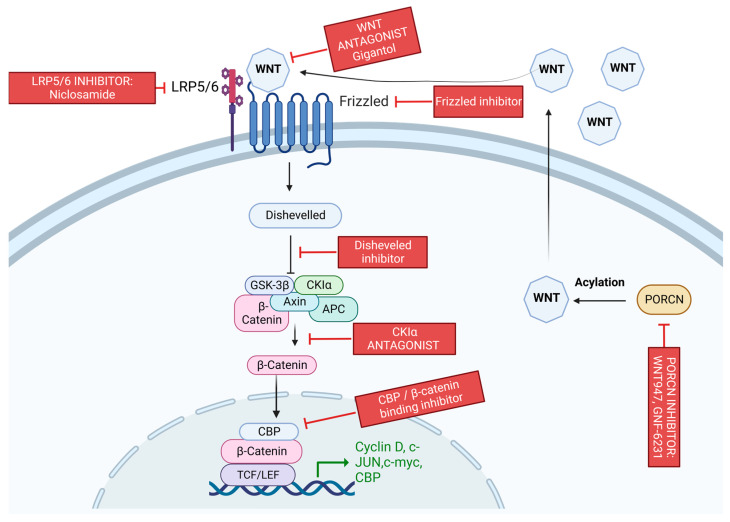
Figure 8.
A diagram of the Wnt signaling pathway. The binding of Wnt to its receptors Frizzled and LRP5/6 inhibits the degradation of β-catenin, which regulates the expression of many genes. Receptor activation leads to the recruitment of the disheveled protein (Dvl). Dvl is then activated via phosphorylation, inducing the dissociation of GSK-3β from axin and causing GSK-3β to be deactivated. The deactivation of GSK-3β inhibits the degradation of β-catenin, allowing it to translocate into the nucleus. The nodes at which current therapies target the pathway are included as well. Created with BioRender.com.