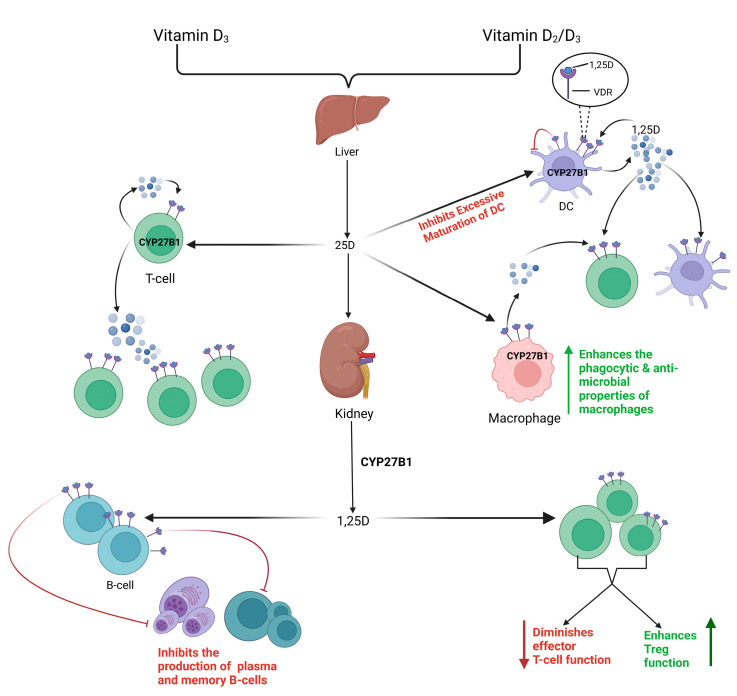
Figure 4.
Vitamin D receptors (VDR) and CYP27B1 are expressed in immune cells and regulate immune responses. The presence of CYP27B1 in antigen-presenting cells (APCs), T cells, B cells, and monocytes allows these immune cells to produce 1,25D, which can bind to its receptor VDR. The 1,25D-VDR complex inhibits the excessive maturation of dendritic cells (DCs). In monocytes and macrophages, 1,25D boosts their phagocytic capabilities and antimicrobial effects. 1,25D contribute to B-cell homeostasis by directly inhibiting memory and plasma cell generation. Furthermore, different forms of vitamin D can affect the proliferation and differentiation of T cells, such as the intracrine conversion of 25D to 1,25D by T cells. T cells may also be affected downstream of the production of 1,25D in APCs and macrophages. 1,25D can elevate the levels of circulating Tregs and reduce the effector functions of cytotoxic and helper T cells, which supports tolerance and highlights its anti-inflammatory properties.