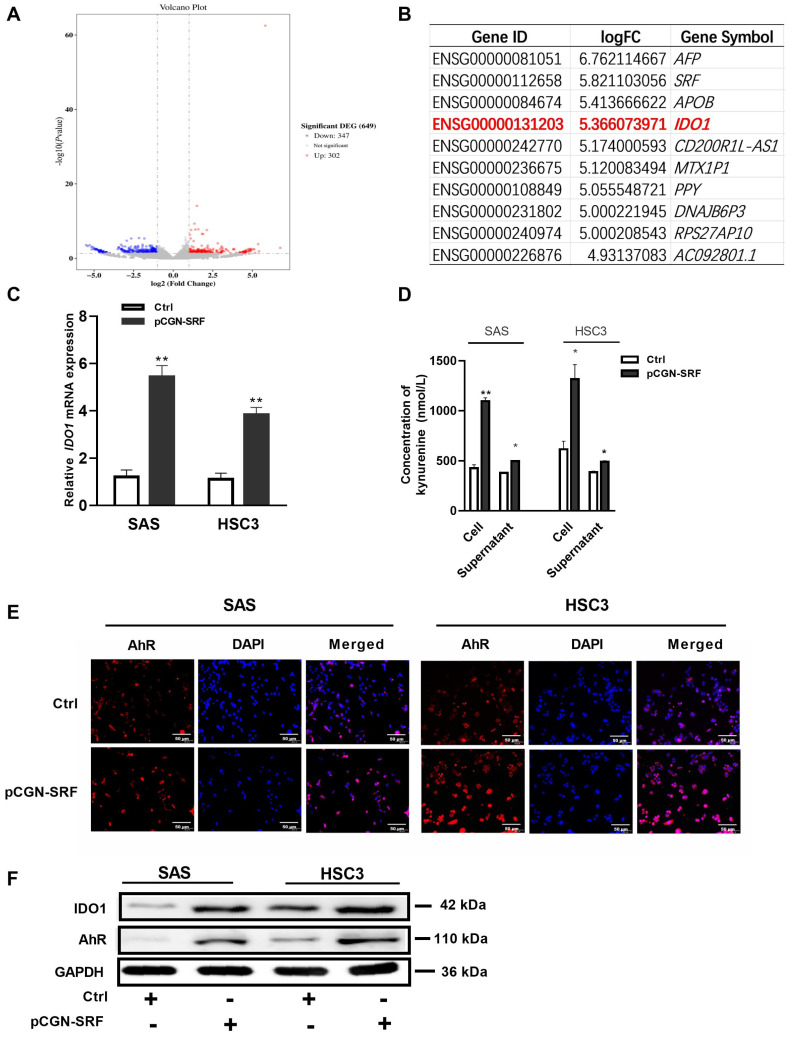
Figure 5.
SRF activates the IDO1/Kyn-AhR signaling pathway in OSCC cells. (A) Volcano plots from RNAseq data of SAS cells infected with the lentivirus vector containing SRF cDNA. The log2FC is plotted on the x-axis and the negative log10FDR (adjusted p) is plotted on the y-axis. represented genes have an FDR < 0.05. Expression levels of 302 mRNAs were upregulated, whereas those of 347 mRNAs were downregulated, in stable SRF-overexpressing SAS cells compared with levels in control cells. (B) Top 10 genes in SAS cells upregulated by the stable overexpression of SRF. The information of IDO1 gene expression was highlighted as red color. (C) qRT-PCR of IDO1 mRNA expression in SAS and HSC3 cells transfected with pCGN-SRF or control vector for 24 h. (D) Kynurenine concentrations in cells transfected with pCGN-SRF for 48 h, measured using ELISA. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 pCGN-SRF group compared with Ctrl group. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of AhR in SAS and HSC-3 cells transfected with pCGN-SRF or control vector for 48 h. (F) Expression of IDO1 and AhR in SAS and HSC3 cells transfected with pCGN-SRF or control vector for 48 h, detected via western blotting. The loading control was GAPDH. Original western blots are shown in Figure S7. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Ctrl, control; DEG, differentially expressed gene; FC, fold-change; FDR, false discovery rate; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; Kyn, kynurenine; OSCC, oral squamous cell carcinoma; RNAseq, RNA sequencing; SRF, serum response factor.